Column What is Lordosis? Its Various Causes and How to Identify and Remedy That Condition that Can Lead to Back Pain, Mental and Physical Issues
August 22, 2024
Excessive arching of the lower back can cause lower back pain as well as other physical and mental ailments.
In this issue, we will discuss the causes of lordosis, how to identify it, and how to remedy it.
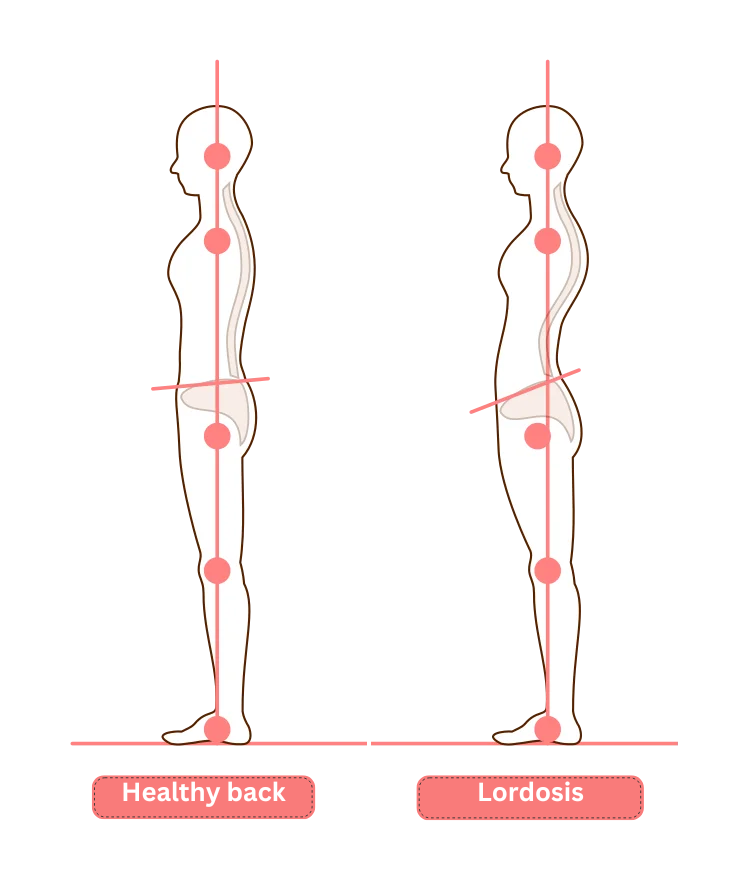
What is lordosis?
lordosis is a condition in which the lower back is overly arched. Technically speaking, this is defined as an “anterior pelvic tilt,” in which the pelvis is tilted forward, causing the sacrum to protrude backward.
How to identify lordosis
You can monitor yourself to see if you have lordosis.
Here are the two main methods to achieve this.
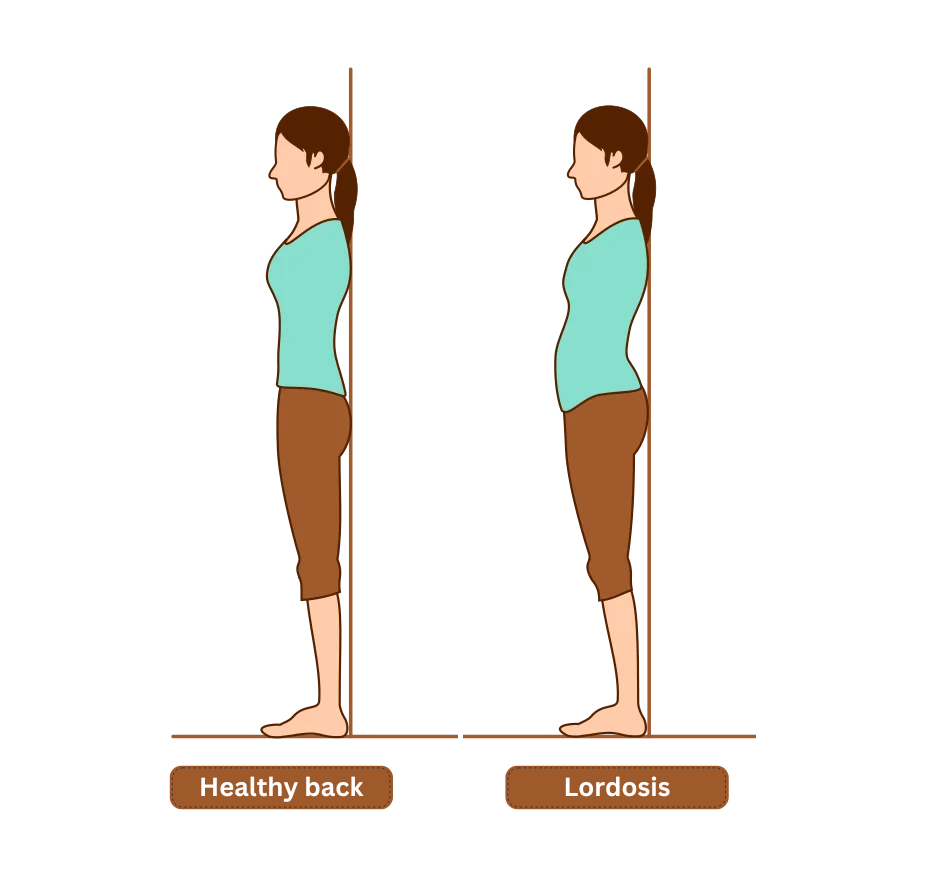
While standing up
Stand with your head, back, and buttocks against a wall, and place your hands in the space between the wall and your lower back. If the gap is barely big enough for your hand to fit in, it is unlikely that you have lordosis. On the other hand, if the gap is large, it is highly likely that the person has lordosis.
While lying on your back
Lie on your back on the floor and put your hand between your lower back and the floor. If there is only a small gap in which your hand can fit, the spine can be considered normal. The larger the gap, the greater the possibility of lordosis.
Also, if you extend your legs while lying on your back and experience increased discomfort or pain in your lower back, you are likely to have a high degree of lordosis. The more discomfort and pain you experience with your legs extended compared to when you stand on your knees, the more advanced your lordosis is.
The causes of lordosis
There are various causes to lordosis.
Muscular imbalance
Basically, lordosis is caused by overworked muscles that make the lower back overly arched. Weak abdominal muscles can also lead to lordosis.
Mutual imbalance between the lumbar and abdominal muscles is one of the causes of lordosis.
Stiff anterior hip joints
On the anterior side of the hip joint are muscles called the iliopsoas and rectus femoris muscles. When these muscles contract and become stiff, the anterior pelvic tilt becomes stronger. As the pelvis becomes more anteriorly tilted, the kyphosis of the lumbar vertebrae also becomes stronger, making it easier to develop lordosis.
Weight gain
Gain in weight causes the abdomen to protrude and the center of gravity to shift to the front of the body. As a result, the body tends to tilt forward when standing. To support the weight of the abdomen and correct the forward leaning posture, the lower back must bend over, resulting in a slouch.
Wearing high-heeled shoes
Wearing high-heeled shoes tends to place more weight on the toes. This causes the center of gravity to tilt forward. This can lead to lordosis as the body tries to compensate and move the tilted center of gravity backward.
Symptoms and medical conditions caused by lordosis
Lordosis can cause a variety of ailments.
Chronic lower back pain
When the muscles that rotate the lower back become overworked and stiff, blood flow is impeded and results in lower back pain. Continued poor posture at work, for example, can easily lead to chronic low back pain.
Lumbar spinal canal stenosis
As the kyphosis of the lumbar spine becomes stronger, the spinal canal in the lower back narrows. This results in compression of the nerves in the lower back, causing numbness and pain in the legs. Symptoms such as difficulty in exerting strength in the legs and inability to walk long distances (intermittent claudication) may occur.
Pisiform muscle syndrome, sciatica
When the pelvis tilts forward due to an overly arched back, the muscle called the piriformis muscle is stretched beyond its normal position.
The stretched pisiform muscle compresses the sciatic nerve that lies beneath the pisiform muscle, causing pain and numbness in the buttocks and legs.
Lumbar spondylolysis
Due to stiffness and lack of strength in the abdominal muscles and other muscles, continued lordosis increases stress on the lumbar spine and increases the risk of lumbar spondylolysis.
How to improve one’s lordosis
To improve lordosis, start by improving your daily activities.
Making sure to sit in the correct posture.
When sitting, bending forward or sitting deeply against a backrest can easily distort the spine. Instead, drawing a mental image of your pelvis being erect and pulled from above will help support your body naturally. Sitting correctly will help improve the discomfort.
You may also reconsider the chairs you usually sit in.
Making sure to stand in the correct way
Just like with correct sitting, correct standing is also important. The chin should be pulled back, shoulders relaxed, the stomach tucked in, and buttocks tightened so that the center of gravity is right in front of the ankles.
To maintain a correct standing posture, a certain degree of muscle strength is necessary. Try to improve your muscle strength by incorporating muscle training into your daily routine.
Avoid wearing high-heeled shoes as much as
possible.
Wearing heels for long periods of time puts a strain on the lower back as it keeps you on your toes. If you have lordosis, it is best to avoid heels altogether.
If you must wear heels, include some time in the middle of the day in comfortable shoes to reduce the strain on your feet and back.
Stretch
Misaligned bones and stiff muscles can affect your posture. Stretching loosens the entire body and helps keep the spine and pelvis in the correct position.
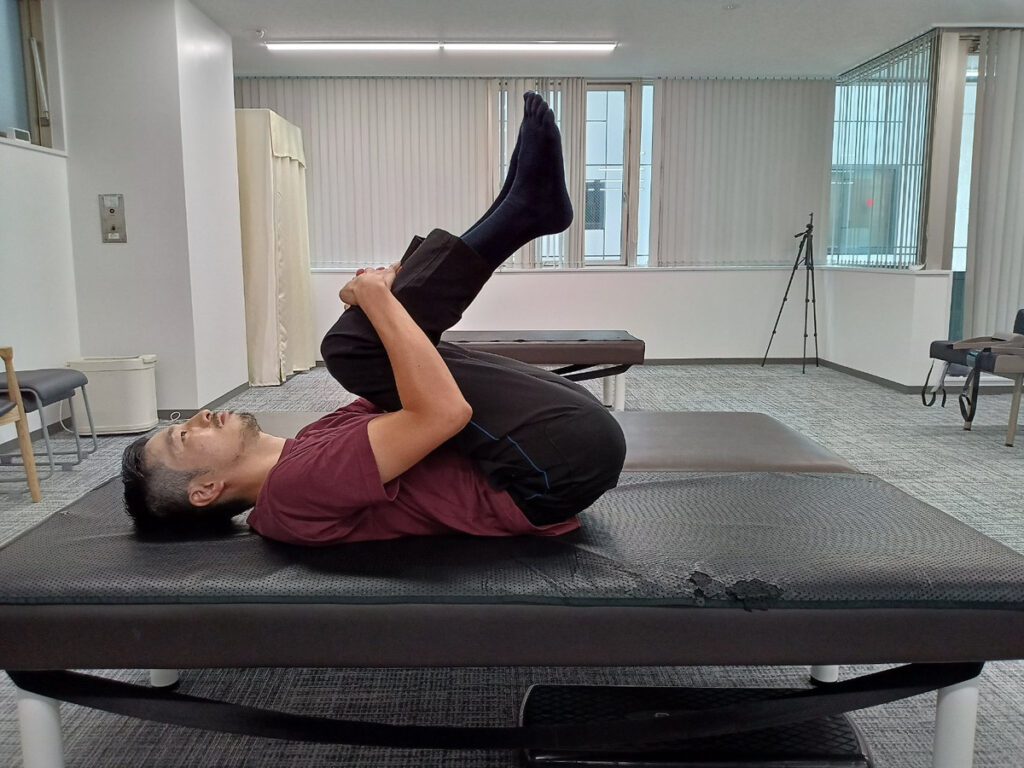
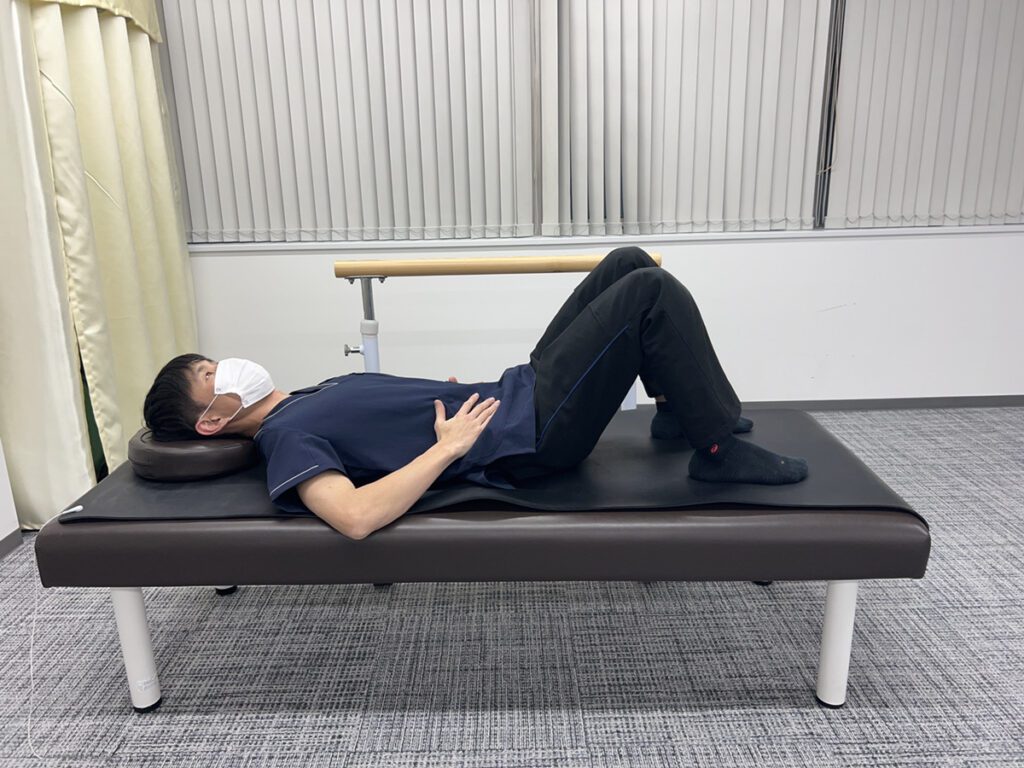
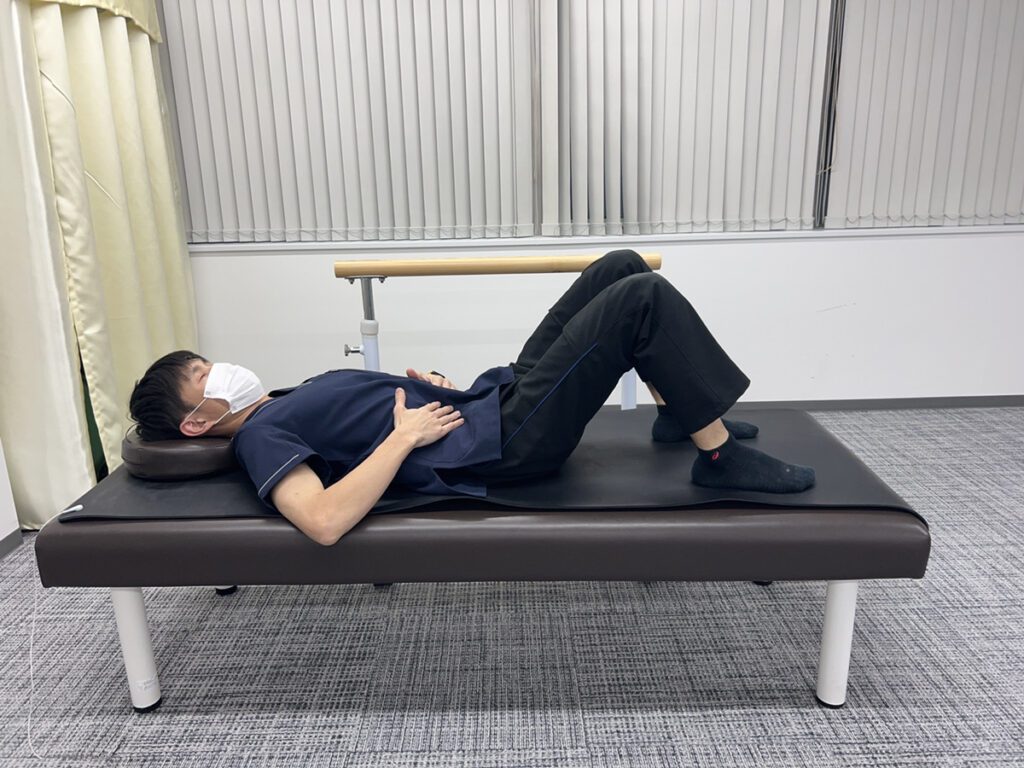
・Stretch holding both knees.
This stretch will help you to avoid overbending at the waist and will also stretch the muscles that support the spine and buttocks.
1. Lie on your back and hold both knees with both hands.
Exhale and bring your knees close to your chest for 10 seconds.
When bringing the knees close to the chest, keep the buttocks off the floor as much as possible.

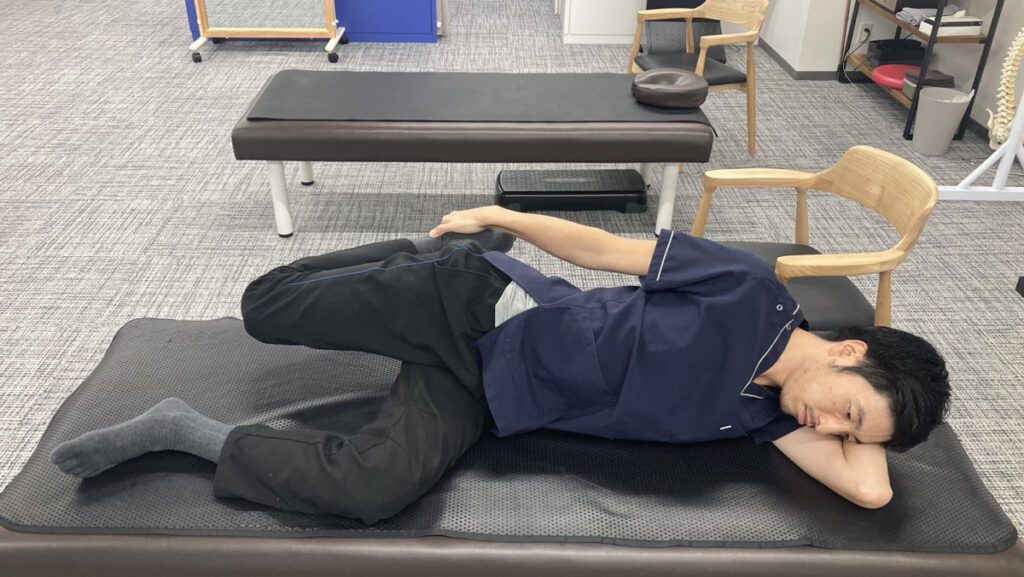
・Stretching the front of the thighs
The muscles at the front of the thigh extend from the pelvis to the knee. When these muscles are strained, the pelvis tilts forward which in turn bends the hips backward.
So, let’s stretch the muscles on the front side of the thighs to reduce the strain on the lower back.
1. Lie on the floor with your body on your side.
2. Hold the ankle on the upper side with your upper hand and pull the heel to the buttock.
* Be careful not to arch your lower back when doing this.
3. When you feel the front thigh muscles stretching, hold for 30 seconds while taking deep breaths.
4. Do the same for the other side of the body.
Do this 3 times a day.
・Drawing
The transversus abdominis muscle, known as the natural corset of the body, is a muscle that supports the vertebrae.
1. Lie on your back and raise both knees.
2. Inhale and exhale loudly as if breathing from the abdomen.
3. Flatten your stomach as you inhale and exhale.
When you exhale, purse your mouth and do it in a long, slow exhale.
Repeat about 10 times.
The treatment at our clinic
When you are experiencing back pain, fundamental treatment may also be necessary.
We perform the Cellgel method to repair damaged intervertebral discs.
With the Cellgel procedure, we inject a drug that fills in the cracks in the disc, which then forms a gel that replaces the cracks, thus providing a fundamental treatment. It is characterized by the fact that the volume of the disc is not reduced, and the drug remains in the disc as a gel-like implant after treatment, thus preserving the disc.
If you are suffering from back pain, please consider taking a consultation at our clinic.
Related Articles
How to Treat Chronic Low Back Pain: Find the right treatment for your condition.
Things You Can do During Work from Home to Prevent Intervertebral Disc Herniation