Column Differences in Symptoms Depending on the Body Site Involved: the Distinction Between Cervical and Lumbar Disc Herniation
July 5, 2024
Disc herniation is the most widely known spinal disorder.
In this article, we will explain the differences between the symptoms of herniated discs in the neck and those in the lower back.
What is disc herniation?
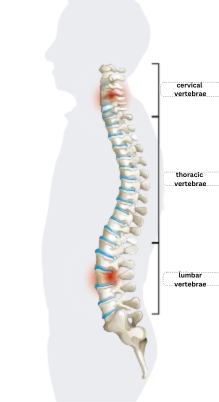
The spine is made up of vertebrae connected with one another, with the cervical vertebrae, the thoracic vertebrae, and the lumbar vertebrae at the top.
When the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc connecting the cervical vertebrae protrudes and compresses the nerves, this is called cervical disc herniation.
When the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc that connects the lumbar vertebrae protrudes, this in turn is called lumbar disc herniation.
The different symptoms of disc herniation
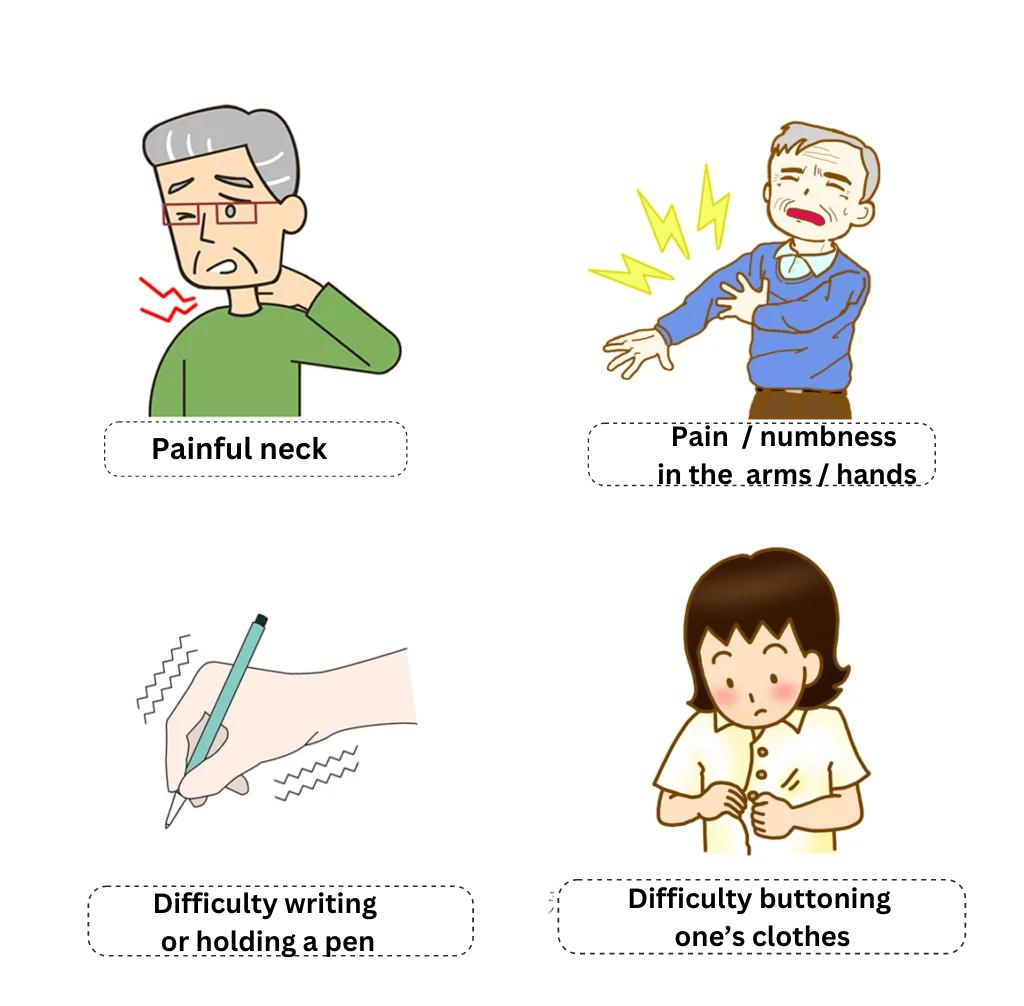
Symptoms of Cervical Disc Herniation
The main symptoms of cervical disc herniation are pain in the neck and shoulders, stiff shoulders, numbness and swelling in the hands, arm fatigue, and muscle weakness. It may also be difficult to write, hold chopsticks when eating, or buttoning one’s clothes.
If the condition progresses, symptoms such as headaches, pain behind the eyes, eyestrain, tinnitus, dizziness, and unsteadiness may occur, and if it worsens further, symptoms in the lower body may also occur (such as walking difficulties and leg stiffness).
Symptoms of lumbar disc herniation
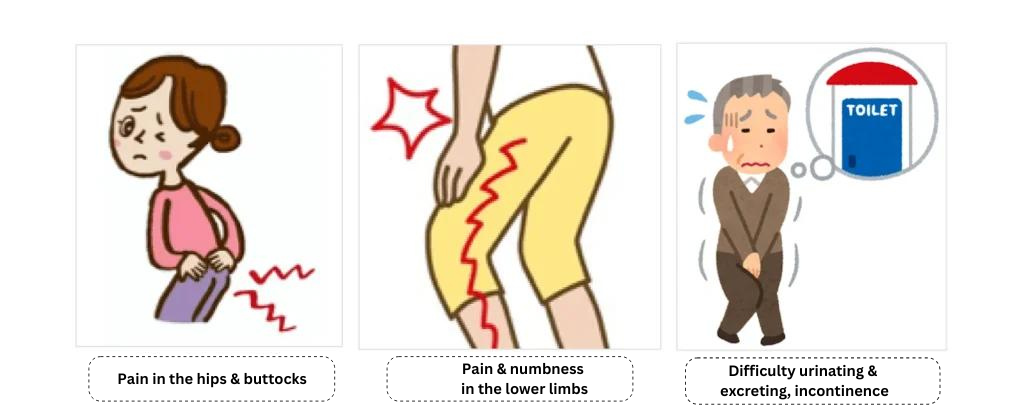
In the case of lumbar disc herniation, the main symptoms are pain and numbness in the buttocks and legs, as well as difficulty moving and difficulty exerting strength. Pain and numbness can occur anywhere in the lower body, but pain in the buttocks and at the back of the thighs is particularly common and is called sciatica, a typical symptom of lumbar herniation.
The spine may then arch sideways, making it difficult to move, and pain may intensify when lifting heavy objects. Symptoms may either appear suddenly or develop gradually.
If the nerves are being compressed very strongly, it may also cause difficulty in urinating or excreting, or even incontinence.
Treatment for disc herniation
The two main treatments for disc herniation, regardless of the body site, are conservative therapy and surgical intervention.
Treatment for cervical disc herniation
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatments for cervical disc herniation include medication, block injections, support braces, and rehabilitation.
Steroidal anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs, muscle relaxants, drugs for the treatment of neuropathic pain, and nerve block injections are used to reduce inflammation and alleviate the pain.
Braces are intended to reduce the burden on the neck, using a cervical collar.
In addition, the use of exercise therapy, stretching, and various physical therapies (such as electrotherapy and ultrasound therapy) is used to improve muscle strength and flexibility and alleviate symptoms.
Depending on the condition, a combination of these methods may be used for treatment.
Surgery
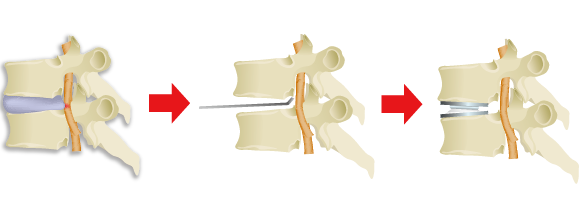
Surgical treatment for herniated discs in the neck generally involves fusion surgery.
Under general anesthesia, the herniated disc is removed through an incision made in the front of the neck, and bone taken from the pelvis or an artificial bone is inserted into the area left empty to firmly hold the cervical vertebrae in place.
This removes the herniation, but it is believed that the discs immediately above and below the herniated disc will come under extreme strain following surgery, and that within 10 years of the operation, a new herniated disc will develop, requiring further surgery. *1
*1 Reference: Nishikawa, T., et al. “A Study of Cases Requiring Reoperation after Anterior Cervical Decompression and Fusion and Laminoplasty,” “Spinal Surgery,” Vol. 26, No. 3, 2012.
Treatment for lumbar disc herniation
Conservative Treatment
As with cervical hernias, the common conservative treatments for lumbar disc herniation are medication, nerve blocks, and physiotherapy.
With medication, the patient will typically take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, opioid analgesics, and neuropathic pain relievers to reduce inflammation and pain. This can help relieve symptoms such as pain.
Nerve blocks are used when drug therapy has not been effective or when the pain is severe. They are effective for relieving pain in specific areas by numbing the nerves.
The aim of physiotherapy is to relieve symptoms such as pain by strengthening the muscles.
Such conservative treatments are generally considered effective for early stage herniated discs.
Surgery
If symptoms fail to disappear after several months of conservative treatment, surgical treatment is then considered.
The most common procedures are the LOVE, MED, and PELD methods. The basic effect of these procedures is to reduce symptoms by removing the herniated disc itself.
In the LOVE method, a 5-10cm incision is made in the back under general anesthesia, and some of the ligaments and vertebral arches are shaved off while avoiding the surrounding nerves, and the herniated part is removed. While there is less risk of missing lesions in this type of surgery, the incision is quite large, so the body is put under a lot of strain, and the hospital stay is also quite long, requiring between 2 to 3 weeks.
In the endoscopic discectomy (MED) procedure, the back is cut open by about 16mm under general anesthesia, and an outer tube and endoscope are inserted to remove the herniated part while checking it with the endoscope. Unlike the LOVE method, there is less muscle dissection and less pain after the operation. In addition, the scar after the operation is smaller than with the LOVE method, and the hospital stay is about 1 to 2 weeks.
Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy (PELD) is performed when the herniated disc is relatively large, and the pain may be quite severe. Under local anesthesia, a tube called an operative tube is inserted through the back, and the herniated disc is removed while checking the area through an endoscope inserted through the tube. The incision is small, the postoperative scar is barely noticeable, and the postoperative pain is minimal.
Treatment on the intervertebral disc
Unlike the conventional surgical method of removing the herniated part, in recent years, the treatment of the damaged intervertebral disc has also been performed on some patients. Unlike surgical operations, it does not require hospitalization, and the treatment can be performed on the same day, but in most cases, such disc treatment is only performed on the lower back.
At our hospital, the PODD and Cellgel methods are used for lumbar and cervical disc herniation.
PODD (Percutaneous Ozone Disc Decompression)
This treatment is indicated for mild hernias that do not respond to conventional conservative treatment and which do not require surgical intervention.
A needle is inserted into the affected disc in the back under local anesthesia, and a mixture of ozone and oxygen is injected through the tip of the needle. Ozone oxidation reduces the volume of the herniated disc, reducing pressure on the nerves. It also has an anti-inflammatory effect on the affected area, so there is little risk of side effects or complications.
The Cellgel method
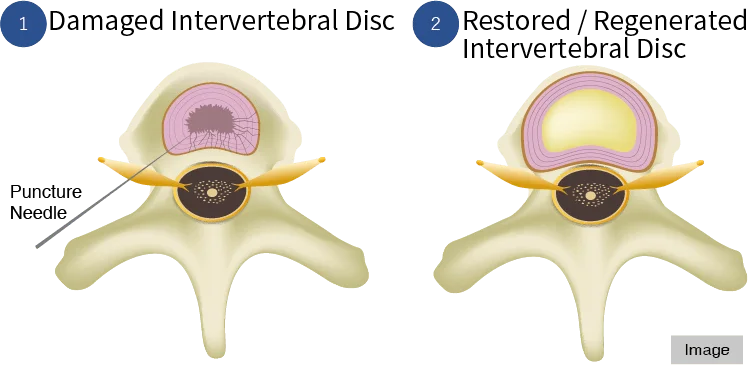
The Cellgel method is a treatment that repairs damaged intervertebral discs.
A drug is injected into the cracked part of the intervertebral disc, which then turns into a gel that fills the crack, preventing further degeneration of the disc and thus providing a fundamental treatment.
The volume of the disc is not reduced, and the drug remains in the disc as a gel-like implant after the treatment, so that the disc is preserved.
The Cellgel method is applicable to both lumbar disc degeneration and cervical disc degeneration.
If you are suffering from lower back or neck pain, please consider coming to our clinic for a consultation.
Related Articles
Prevention is the best medicine! What you should be careful of to avoid herniated discs