Column Are the Recurrence Rates Really that Low? Differences in Recurrence Rates Between the Florence Method and Surgical Procedures
April 26, 2024
The most prevalent treatment for lumbar spinal canal stenosis is usually surgery.
At our clinic, on the other side, we offer the Florence Method, an advanced treatment for spinal canal stenosis.
In this article, we will explain the difference between the Florence method and common surgery.
The surgical procedures: lumbar laminectomy and spinal fusion
Lumbar laminectomy and spinal fusion are the most common surgical procedures performed for spinal canal stenosis.
Lumbar laminectomy is performed under general anesthesia using an endoscope. A 4 cm incision is made on the skin of the back, and part of the vertebral arch and the thickened Ligamentum Flavum are removed to relieve nerve compression and widen the spinal canal.
Spinal fusion is performed under general anesthesia by making a 3 to 4 cm incision in the skin of the back, removing the degenerated intervertebral disc, and then inserting a cage to secure the vertebrae in place with screws and rods. It may be performed consecutively to a lumbar laminectomy.
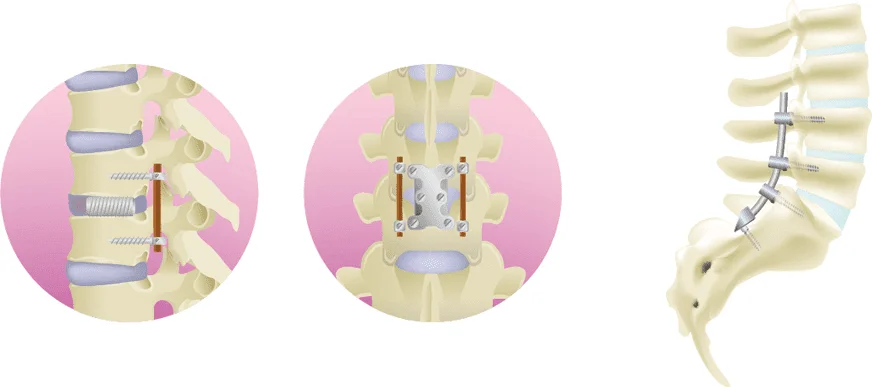
Details of the process after a surgical procedure
Surgical spine procedures require to be hospitalized between one and two weeks. The more sites are operated on, the longer the hospital stay will be.
The day after the surgery, it will be checked that the patient can move normally, like getting up from bed and sitting down, and if the postoperative course is satisfactory, walking exercises and daily activities may be performed.
For the first two weeks after surgery, the patient must wear a corset and practice only simple movements.
After that, desk work or driving a car will be possible.
Heavy labor will be difficult until two months after surgery, and bicycling and running can be started three months after the surgery.
Sports can also be resumed 3 months after the surgery, except for the more strenuous sports that involve collisions or falls.
What is the Florence Method?
The Florence Method is a minimally invasive, low-risk treatment for scoliosis. A spacer is percutaneously implanted under local anesthesia and sedation to widen the narrowed spinal canal.
The spacers are inserted to stabilize the vertebrae while maintaining spinal rotation and flexion, widening the spinal canal, and reducing the protrusion of the intervertebral discs and the thickening of the Ligamentum Flavum. As the narrowed spinal canal widens, symptoms such as pain and numbness are eliminated.
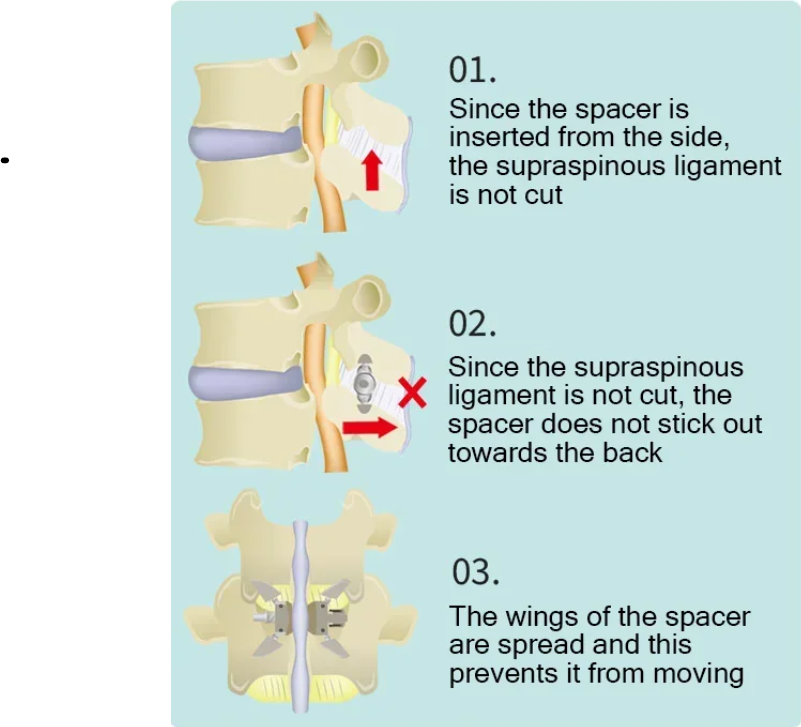
Details of the process after the Florence Method procedure
The Florence Method does not require any hospitalization and is performed as a same-day treatment.
After being treated, patients rest for 2 to 3 hours and can walk home on the same day of treatment.
Daily activities are possible from the next day, but it is recommended to wait for one week for driving, and two weeks for desk work.
Light exercise is allowed two weeks after treatment, and weight training after 3 months.
Recurrence rates of the Florence Method vs. surgical procedure
Recurrence rate for Surgery
It is reported that 8% of patients will require re-operation within 2 years, and 23% within 10 years after receiving a surgical treatment for scoliosis. (*1)
The most common causes of reintervention are recurrence of stenosis at the surgical height, inadequate decompression, and further narrowing of the intervertebral foramen. (*2)
(*1): James N. Weinstein, et al. Surgical versus Nonsurgical Therapy for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. The New-England Medical Review and Journal, 358(8), 2008. Steven J Atlas, et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Surgical and Nonsurgical Management of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: 8 to 10 Year Results from the Maine Lumbar Spine Study. Spine, 30(8), 2005.
(*2): Morimoto, T. et al. “A Study of Reoperation Cases of Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis,” The Journal of Neurosurgery, Vol. 22, No. 12, 2013.
As mentioned above, because surgical procedures remove bone and ligaments, there is a high risk of injury to ligaments and muscles, as well as bone damage, incurring a high recurrence rate of symptoms after surgery.
Recurrence rate of the Florence Method
The Florence method is performed under local anesthesia at minimal risk, and since it is a percutaneous procedure requiring only a 1-2 cm skin incision, there is no damage to ligaments or muscles. As a result, the recurrence rate is extremely low. Studies of the Florence Method at medical facilities around the world have shown no reports of post-treatment complications. (*3)
(*3): Luca Jacopo Pavan, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes following insertion of a novel removable percutaneous interspinous process spacer: an initial experience. Spinal Neuroradiology. 64(9), 2022. Stefano Marcia, et al. Feasibility, safety, and efficacy of a new percutaneous interspinous device: a retrospective multicenter study. Neuroradiology. 2024.
If you have been diagnosed with spinal stenosis and are suffering from back pain or intermittent claudication, please consider reserving a consultation with us.
Related Articles
The Florence Method: Introducing Our Innovative One-Day Treatment Method for Spinal Canal Stenosis
Which is better, the Florence method or the Cellgel method?
We read the studies on the Florence Method, which is currently being researched around the world!