Column Conservative Treatments for Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis — Understanding the Differences Between Exercise, Medication, and Injections
November 13, 2025
Spinal stenosis, along with disc herniation, is one of the most common spinal disorders
In addition to low back pain, it can cause pain and numbness in the legs, as well as intermittent claudication — a condition in which pain develops in the hips or legs while walking, eases with rest, and returns when walking resumes — significantly affecting daily life.
In this article, we explain the main conservative (non-surgical) treatments for spinal canal stenosis.
What Is Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis?
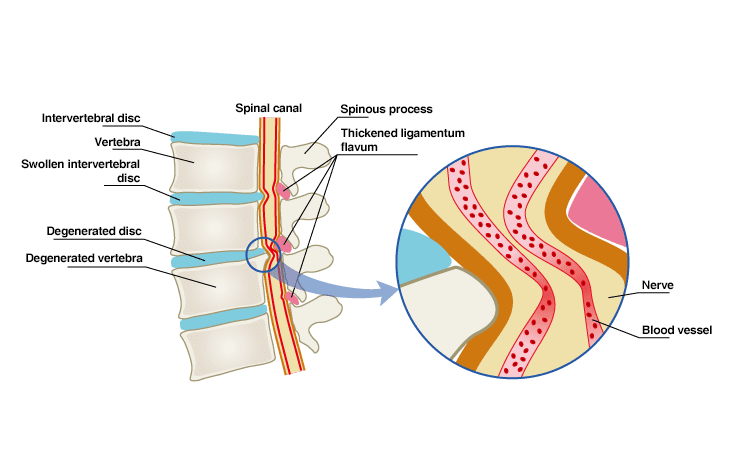
Spinal canal stenosis is a condition where the spinal canal (the passageway for the spinal cord within the spine) or the intervertebral foramen (the exit for peripheral nerves) becomes abnormally narrowed, leading to compression of the spinal cord or nerve roots.
Symptoms
Key symptoms include low back pain, numbness in the buttocks and legs, intermittent claudication, and muscle weakness or reduced motor function.
Symptoms generally develop gradually. In severe cases, it can cause loss of bladder/bowel control, sexual dysfunction, muscle weakness, and difficulty walking.
Causes
The condition is generally caused by repetitive strain on the spine from activities involving the lower back, or by obesity, which increases the load on the vertebrae.
Over time, the vertebrae deform, and the ligamentum flavum (a spinal ligament) thickens, compressing the nerves.
Because it develops gradually, many patients are unaware of the condition until symptoms become noticeable.
Conservative Treatments for Spinal Canal Stenosis
Once diagnosed with spinal stenosis, conservative treatment is typically the first approach to reduce symptoms.
Medication
When pain or numbness is severe, anti-inflammatory pain relievers are prescribed.
Other medications, such as prostaglandin derivatives, may also be used to improve blood flow to the nerves, helping to reduce pain and numbness.
Depending on the severity, the medication may be administered via injection or IV drip in addition to oral form.
Note: The effect of medication varies significantly among individuals. Always consult with a specialist or your primary doctor and avoid self-medicating.
Nerve Block Injections
This involves injecting a local anesthetic or steroid directly near the nerve root that is causing the pain.
By blocking the pain signals transmitted by the nerve, it can interrupt pain transmission and relieve inflammation.
It also helps improve blood flow, reduce muscle tension, and prevent secondary pain due to nerve irritation.
While nerve blocks can provide immediate relief, they carry potential risks such as temporary nerve irritation, so treatment should always be discussed with a qualified specialist.
Physical Therapy
Improving spinal mobility through targeted exercises can help reduce symptoms of spinal canal stenosis.
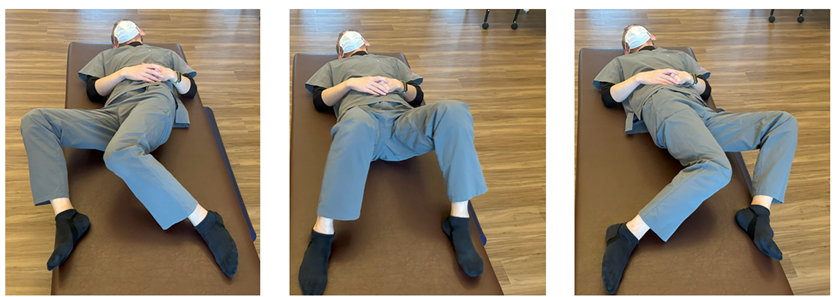
・Exercise for Improving Spinal Mobility
This exercise focuses on improving the movement of the pelvis and spine for increased flexibility.
1. Lie on your back with both knees bent.
2. Slowly lower both knees to one side, moving in the order: knees → pelvis → lower back.
Focus on the sensation of the pelvis moving first, followed by the lower back.
Perform this continuously and slowly for about 2–3 minutes.
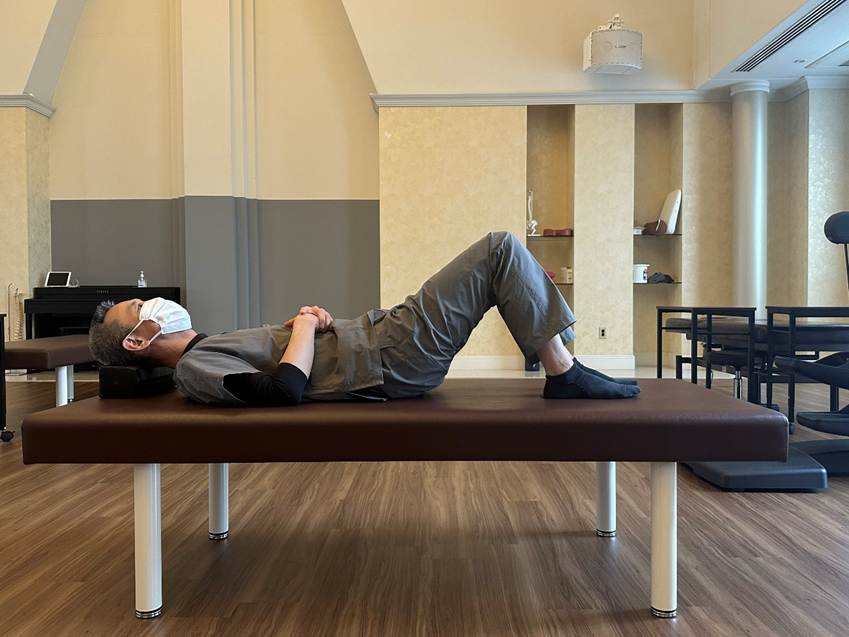
・ Exercise for Activating the Core and Supporting the Spine
This exercise aims to improve spinal movement using abdominal strength, which helps relieve lumbar strain during activities like standing up and walking.
1. Place your hand just below your navel.
2. Exhale through your nose while drawing the area under your hand inward (sucking in your stomach).
3. While keeping your stomach drawn in and your back flat on the floor, slightly lift your buttocks.
4. Slowly lower your buttocks back down.
5. Focus on the motion starting from the pelvis and extending through the lower spine as you lift your buttocks.

Advanced Treatment Options at Our Clinic
If conservative treatments fail to provide relief, our clinic offers two advanced, minimally invasive options for spinal stenosis: the Florence Method/Q-Florence Method and the Cellgel Method.
The Florence & Q-Florence Methods are low-risk, minimally invasive treatments performed under local anesthesia and sedation.
A device is percutaneously inserted under local anesthesia and sedation to widen the narrowed spinal canal. The device can be removed for some time after the intervention if needed.
It stabilizes the vertebrae while preserving spinal rotation and flexion, widening the spinal canal, and suppressing disc protrusion and ligamentum flavum hypertrophy. This relief of compression resolves the pain.
These methods are ideal for patients who do not respond to conservative therapy and wish to avoid open surgery under general anesthesia.
👉 Click here for more on the Florence Method
Spinal stenosis is often triggered by a cracked disc allowing the nucleus pulposus to protrude and narrow the canal. If the crack in the disc is not repaired, recurrence is likely.
The Cellgel Method involves injecting a specialized gel-like agent into the damaged area of the disc.
This material then solidifies into a soft implant, filling and sealing the cracks, providing a fundamental treatment while preserving disc volume and function.
👉 Click here for more on the Cellgel Method
Our clinic also provides specialized rehabilitation programs tailored to patients with chronic back pain, suitable for a wide range of age groups and conditions.
👉 Click here for more on the OJ Wellness Center
If you are suffering from spinal stenosis, please consider a consultation at our clinic.
Related Articles:
Feeling uncertain after diagnosis? Understanding second opinions for spinal canal stenosis
Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis: What is Actually Happening to my Body?
Why Do the Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis Differ From Person to Person?
Self-Check: Assessing the Progression of Spinal Stenosis
The Relationship Between Spinal Canal Stenosis and Leg Numbness
Diagnosis and Treatment of Spinal Stenosis: Why Early Detection is Critical