Column Risks and Solutions Concerning Spinal Canal Stenosis: What are the Most Common Symptoms Observed Among the Elderly Patients?
January 10, 2025
Spinal canal stenosis is a condition in which the nerve pathway (= spinal canal) in the spine constricts. According to a survey report on spinal surgery by the Japanese Society for Spine and Spinal Cord Diseases, it is said to be the most common spinal disorder (*1).
(*1: ) Yutaka Nohara et al, “Report on Spine Surgery Survey by the Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research,” Journal of the Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research, Vol. 15, No. 2, 2004.
In this article, we will explain the possible risks and different solutions concerning lumbar spinal canal stenosis.
What is spinal canal stenosis?
Spinal canal stenosis is a constriction of the nerve pathway (i.e., the spinal canal) that occurs inside the spine.
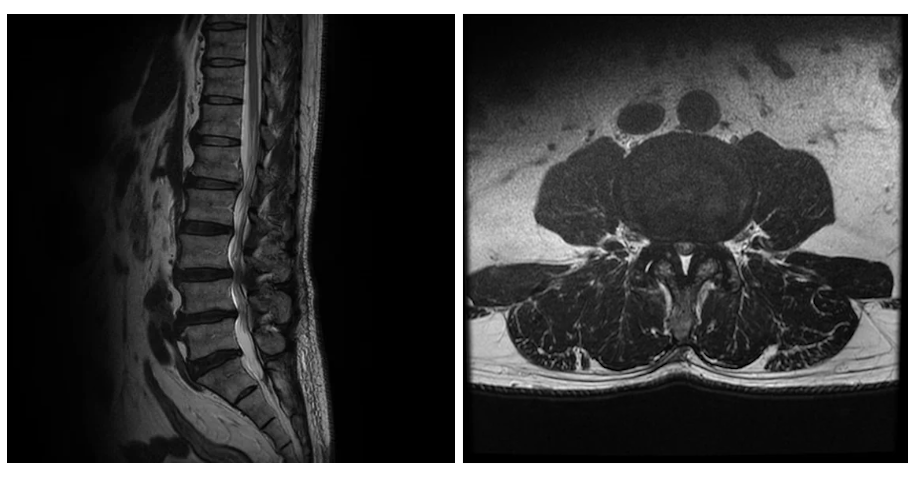
Although the narrowing of the spinal canal can occur in any part of the spine, it most frequently occurs in the lower back (lumbar spinal canal stenosis) and the neck (cervical spinal canal stenosis). Both are more prevalent in people over the age of 50 and also tend to be more common in men.
When the spinal canal constricts over a wide area in the neck, chest, and lower back, it is known as extensive spinal canal stenosis and is considered an incurable disease.
Causes of Spinal Canal Stenosis
The main causes of spinal canal stenosis are age-related degeneration of the intervertebral discs and deformation of the bones and ligaments.
Age-related changes initiate the degeneration of the intervertebral discs, and as the discs degenerate, the nucleus pulposus protrudes outward through a crack in the annulus fibrosus, resulting in disc herniation. When the spinal canal is compressed by a herniated disc, it results in spinal stenosis.
In addition, as the disc degeneration progresses, the disc becomes thinner and loses its cushioning function due to its loss of water content contained within the disc. That can lead to instability and misalignment of the spine. As the spine shifts its position, the spinal canal can become narrower, resulting in spinal stenosis.
Although rare, some people may also have a congenitally narrow spinal canal.
Symptoms of Spinal Canal Stenosis
When the spinal canal narrows and the nerves are compressed, symptoms such as pain, numbness, and weakness in the lower back and lower extremities may occur.
If symptoms are present only on the right side of the body, it means that the nerve root on the right side is compressed, and if symptoms are present on the left side, the nerve root on the left side is compressed. If there are symptoms on both sides of the body, then the cauda equina nerve is compressed.
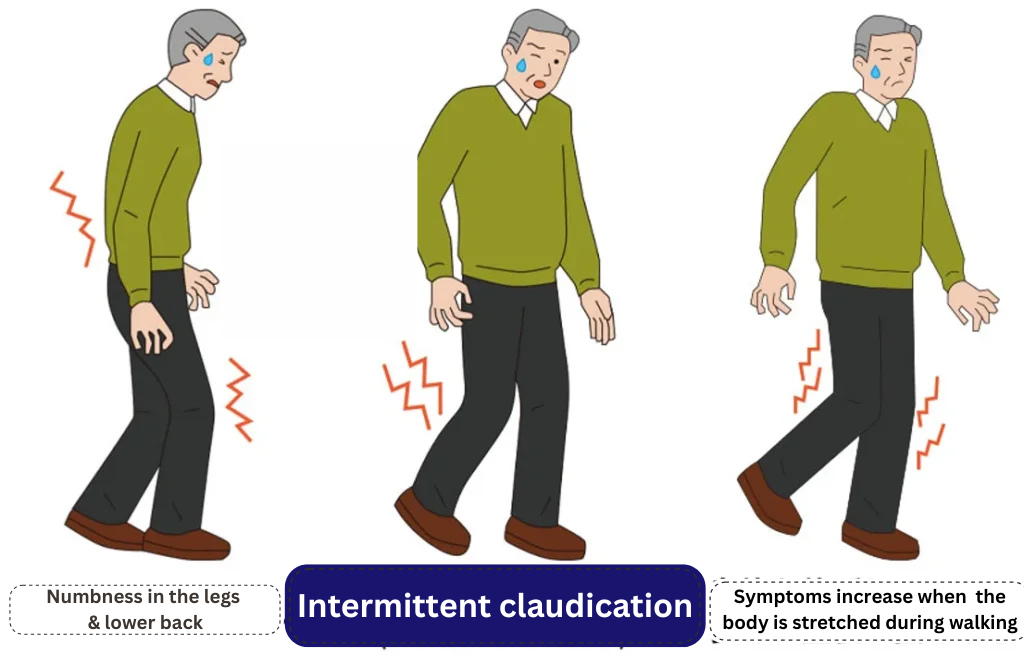
A typical symptom of spinal stenosis is intermittent claudication.
Intermittent claudication is a condition in which the lower limbs become numb or weak during walking, making it impossible to walk, but after a short rest by squatting or sitting down, the patient will be able to walk again.
The more advanced the stenosis, the shorter the distance that can be walked.
As spinal stenosis progresses, symptoms as various as loss of strength in the lower limbs, hot flashes in the perineal area, difficulty to urinate or, conversely, an inability to hold urine may occur.
How to remedy to spinal canal stenosis?
The most common treatment for spinal canal stenosis is spinal surgery (lumbar laminectomy and spinal fusion), but many people prefer to avoid surgery because of the high risks involved.
The following includes a list of non-surgical measures that can be taken.
Physical Therapy
Improving the movement of the spine can alleviate the symptoms of spinal canal stenosis.
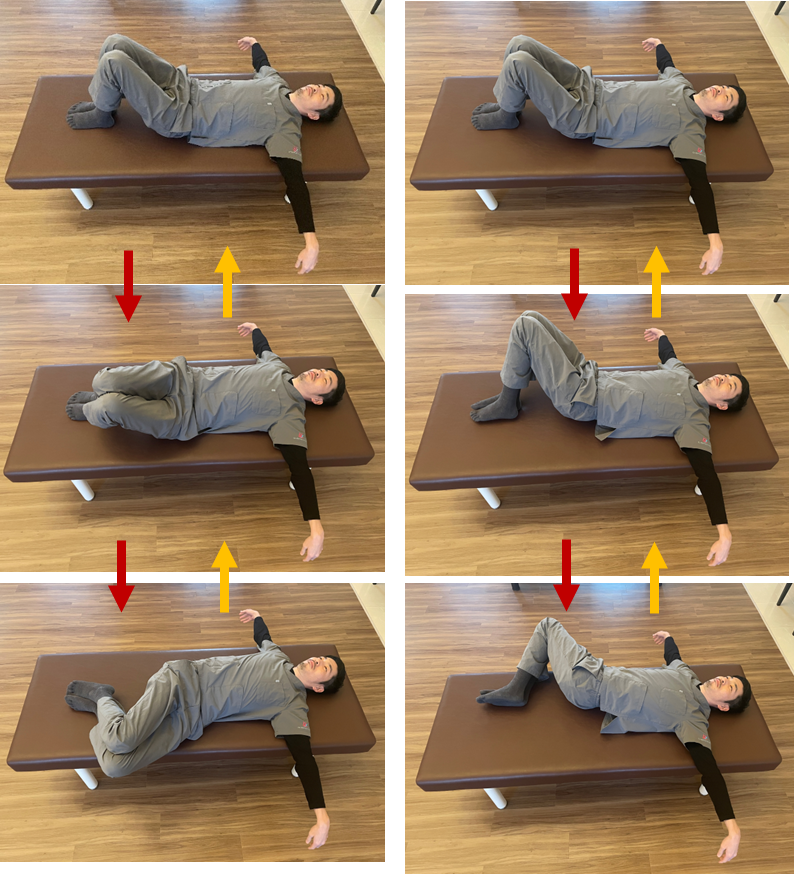
・Exercise to improve spine mobility
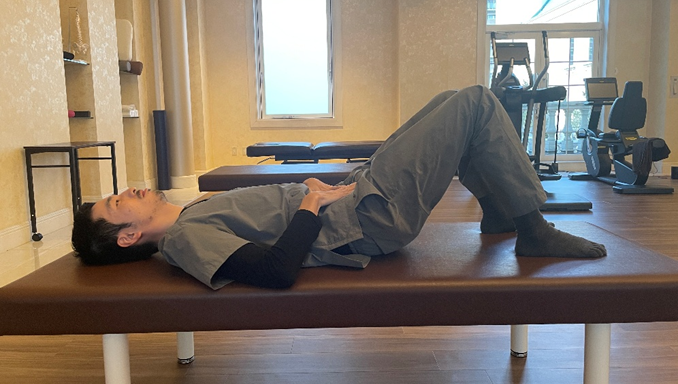
The purpose of this exercise is to improve the movement from the pelvis to the spine by moving the body with flexibility.
- Lie down on your back with both knees up and slowly tilt them down.
2. As you roll over, be mindful to move the knees, pelvis, and hips, in that particular order.
Be sure to focus on moving the pelvis first, then the hips.
3. Perform the exercise slowly and continuously for 2 to 3 minutes without stopping.

・Exercise to improve spine mobility
The purpose of this exercise is to make the spine move by using the strength in the abdomen.
By improving the movement of the spine, the strain on the lower back caused by standing up and walking can be relieved.
1. Place your hands below your navel.
2. Exhale through the nose and gently press down on the area where the hands are placed.
3. While doing this, lift your buttocks without lifting your back.
4. Slowly lower your buttocks after lifting them.
5. Concentrate on moving the lumbar vertebrae (the lower back spine) away from the pelvis when you lift your buttocks.
Minimally invasive treatment
The Florence, the Q-Florence Method and the Cellgell Method can also be used in the treatment of spinal canal stenosis.
Both of these procedures are minimally invasive and cause little physical strain. They are recommended for patients who wish to avoid surgical procedures that require general anesthesia, such as spinal fusion.
・The Florence and Q-Florence Methods
The Florence and Q-Florence methods are minimally invasive, low-risk treatments for spinal stenosis.
Under partial anesthesia and sedation, a device is percutaneously inserted to widen the narrowed spinal canal.
The device is inserted to stabilize the vertebral body while maintaining spinal rotation and flexion, widening the spinal canal and reducing disc protrusion and thickening of the ligamentum flavum . Pain is eliminated as soon as the narrowed spinal canal is widened.
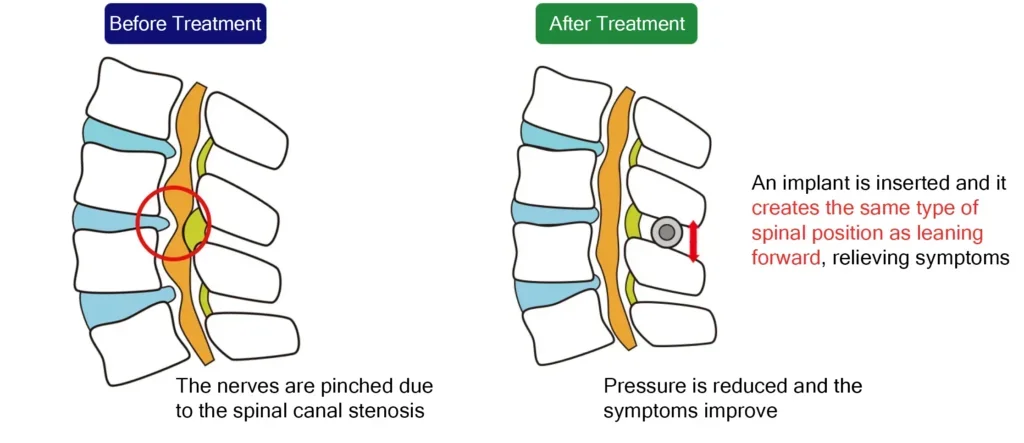
The Q-Florence method (in Japanese)
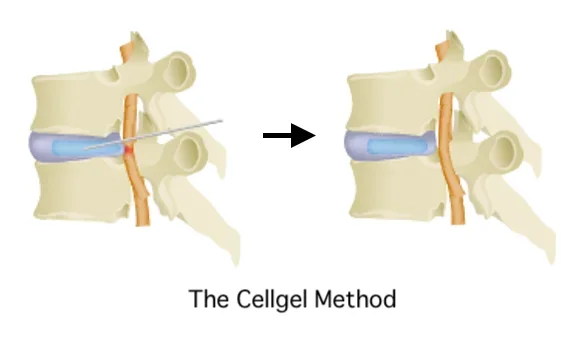
・The Cellgel Method
Spinal canal stenosis occurs when a crack in an intervertebral disc occurs, causing the substance inside to come out and protrude, the protrusion in turn narrowing the spinal canal. If the cracked disc is not repaired, it may herniate again or cause the spinal canal to narrow again.
The Cellgel Method used at our clinic provides a fundamental treatment by injecting a drug that fills in the cracks of the disc, before turning into a gel and repairing the cracks. It is characterized by the fact that the volume of the disc is not reduced and the drug remains in the disc as a gel-like implant after treatment, thus preserving the disc.
If you have ever been diagnosed with spinal canal stenosis, please consider a consultation at our clinic.
Related articles
The Different Symptoms of Spinal Canal Stenosis: If You Have Any of These, It’s a Red Flag!
How to Spend Time after Spinal Stenosis Surgery
Is it already too late! ? What should I do about spinal canal stenosis that has been left untreated?
How to Deal with Stenosis Pain and Numbness
What are the Various Complications Possible With Spinal Stenosis?
During an Operation for Spinal Stenosis… Exactly Who is Doing What?
Why Do the Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis Differ From Person to Person?