Column Could This be The Sign of a Serious Disease that is Undetected? The Relationship Between Lower Back Pain and Internal Organs
August 29, 2024
The causes of lower back pain can be various.
When you suffer from lower back pain, it is often thought that it is caused by a lumbar disease, when it can also be caused by internal organ diseases that have little to do with the lower back.
In this article, we will explain the relationship between lower back pain and internal organs.

Low back pain caused by internal organs
Low back pain can be caused by internal organ fatigue or internal organ disease.
Internal organ fatigue as the cause
Excessive drinking, overeating, and lack of sleep can cause low back pain.
Internal organs repeatedly digest, absorb, and metabolize food, but if the amount of food entering the body is too large, the internal organs will be put under too much strain. This will cause fatigue to build up, and the function of the internal organs will gradually decline.
When fatigue builds up, the internal organs slowly become stiffer, pressing on the bones and muscles and causing pain.
In addition, the internal organs can start to sag downwards, which can prevent blood from circulating properly throughout the body.
Internal organ diseases as the cause
If you have an internal organ disease, you may also experience lower back pain.
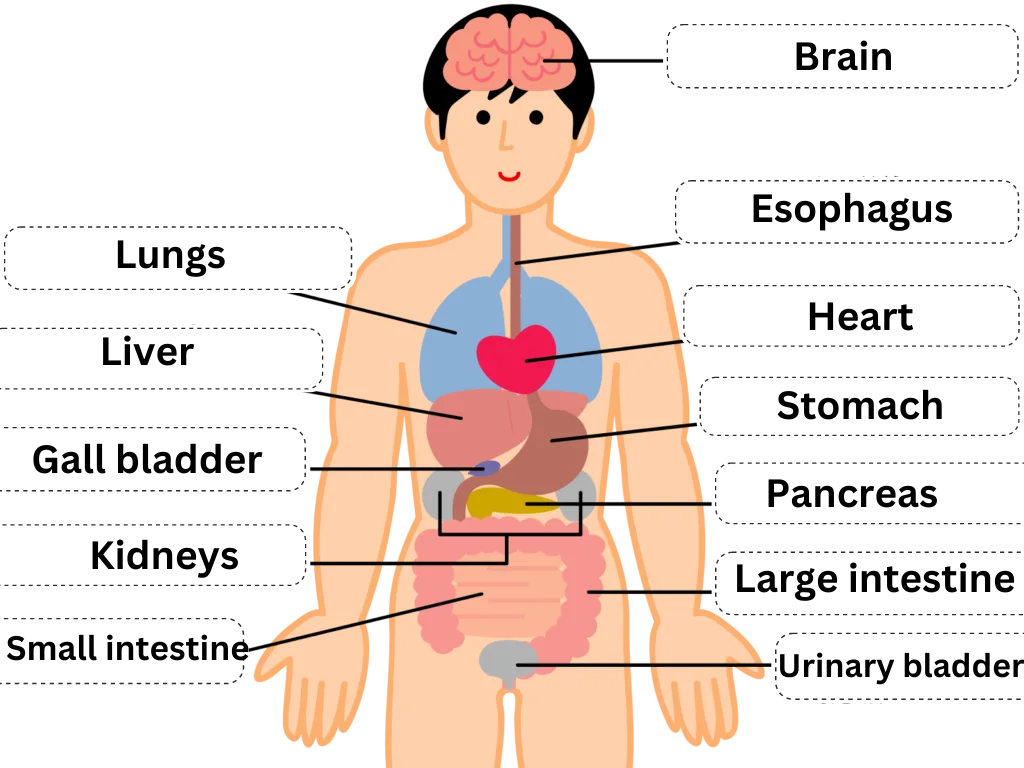
Digestive system diseases
Back pain can occur in cases of diseases such as stomach and duodenal ulcers, gallstones, cholecystitis, and pancreatitis. In addition to back pain, symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloody stools, nausea, and vomiting may also occur.
Diseases of the urinary system
Diseases that can cause lower back pain include urinary tract stones, kidney stones, pyelonephritis, and prostate cancer. Symptoms of dysuria and hematuria are characteristic.
Diseases of the gynecological system
Lower back pain can also occur in endometriosis and uterine cancer. Irregular vaginal bleeding can also occur.
Diseases of the circulatory system
When a person has a myocardial infarction, they may experience a tight, squeezing pain in their back or lower back. In addition, in the case of a dissecting abdominal aortic aneurysm, a person may experience sudden, severe pain in their lower back and abdomen.
Criteria for determining the cause of pain
due to internal organ disease
Depending on the symptoms and location of the pain, it may be possible to determine whether the cause is an internal organ disease.
For example, if you have pain on the right side of your lower back, you may have appendicitis (the appendix), a kidney that has moved down (or dropped), liver disease or liver cancer.
If you have pain on the left side, you may have pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, nephritis, stomach ulcers or uterine fibroids.
Another criterion for diagnosis is whether the pain is present at rest.
Low back pain caused by internal organ disease, like sudden lower back pain, often comes on suddenly and is very painful, but in the case of sudden lower back pain, the pain may be relatively less severe when resting, whereas in the case of internal organ disease such as ureteral calculi, the pain does not change even when resting.
If you experience back pain, do not make your own diagnosis, but be sure to visit a medical facility for an examination.
Treatment at our clinic
Our clinic provides treatment for lower back pain caused by damage to the intervertebral discs.
In our clinic, we use the Cellgel method, which involves injecting a substance that fills the cracks in the intervertebral disc, causing it to become gel-like and fill the cracks, allowing for a fundamental treatment. The volume of the intervertebral disc does not decrease, and the substance remains in the intervertebral disc as a gel-like implant after treatment, so the intervertebral disc is preserved.
If you are suffering from lower back pain, please consider a consultation at our clinic.
Related Articles
The structure of the spine and types of diseases. Which of these is your condition and cause?