Column The Structure of the Spine and the Different Types of Disorders Related to it: Which One Is Causing Your Symptoms?
June 09, 2023
The structure of the spine
The spine consists of three main structures: (1) the bones (vertebrae), (2) the intervertebral discs, and (3) the nerves.
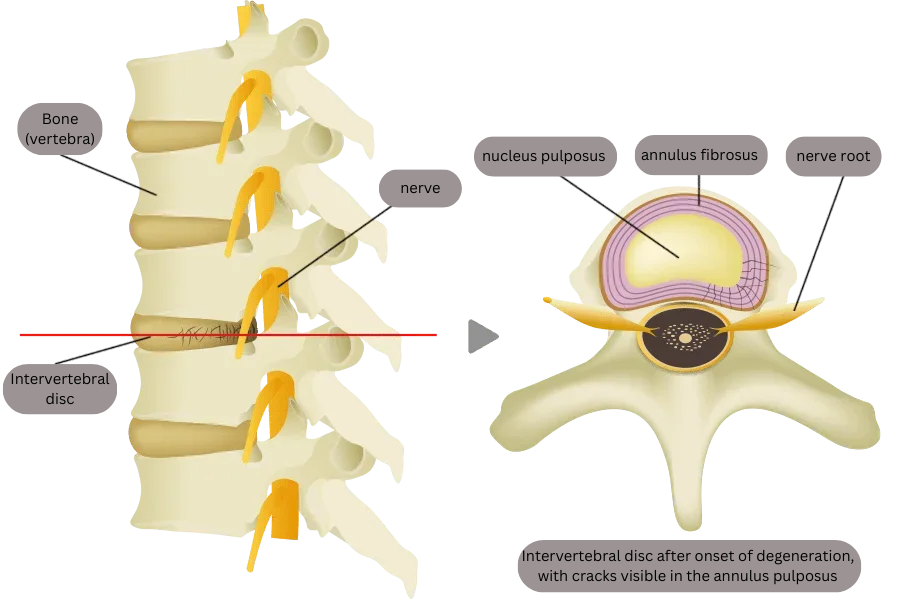
The intervertebral disc is located between the vertebral bodies and is composed of two layers: the annulus fibrosus and the nucleus pulposus. The annulus fibrosus is a structure composed of alternating fiber tissues capable of absorbing impacts from multi-directional movements. The nucleus pulposus is filled with water, which also helps with the cushioning function.
The different types of spinal conditions
Degeneration begins when the intervertebral disc is unable to maintain its original shape due to injury or other causes, resulting in a loss of disc function and symptoms such as back pain. This is known as disc degeneration.
As the degeneration progresses, the nucleus pulposus protrudes outward through a crack in the annulus fibrosus, resulting in a herniated disc.
In turn, the herniated disc compresses the spinal canal, resulting in spinal stenosis.
The more disc degeneration progresses, the more water contents become depleted in the disc, and the thinner and thinner the disc becomes and the more volume it loses.
As this occurs, the vertebrae become more likely to collide with each other. Repeated collisions result in the formation of bone spurs called osteophytes and deformation of the vertebral bodies themselves, leading to osteoarthritis of the lumbar spine.
In addition, as the intervertebral discs lose their cushioning function, the spine becomes unstable (lumbar instability) and may become misaligned (spondylolisthesis).
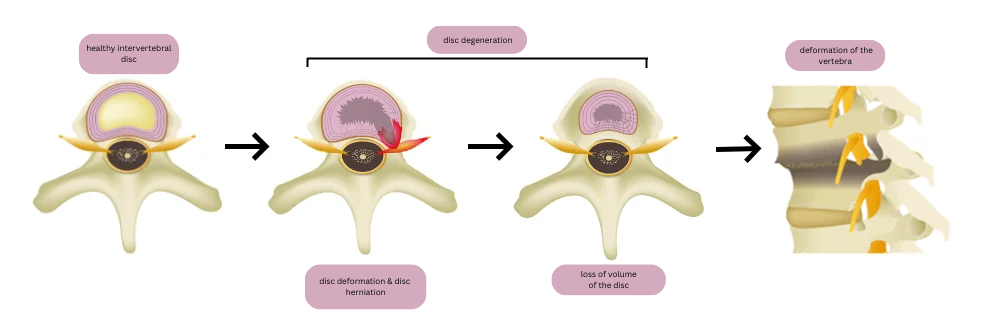
In this way, various spinal conditions can arise from the degeneration of the intervertebral discs.
Characteristic symptoms of each condition
Symptoms of disc degeneration: back pain only.
If the only apparent symptom is back pain, this is symptomatic of intervertebral disc degeneration.
This type of lower back pain is most likely to occur while leaning, forward bending, twisting, and other movements, as well as when lifting heavy objects.
Symptoms of disc herniation: pain in the lower back, pain and numbness in the buttocks and legs.
If, in addition to pain in the lower back, you also have symptoms of pain and numbness in the buttocks and legs, you may have a herniated disc.
In the case of a lumbar disc herniation, the pain is relieved when the back is extended or when sleeping, but when the back is rounded or bent over, the pain and numbness become more intense due to nerve compression.
Symptoms of spinal stenosis, spondylolisthesis, and osteoarthritis of the lumbar spine: pain in the lower back, pain and numbness in the buttocks and legs, intermittent claudication, etc.
In addition to pain and numbness, patients with spinal stenosis, spondylolisthesis, and osteoarthritis of the lumbar spine may also experience symptoms such as gait disturbance. The distinguishing feature of this condition is intermittent claudication, which is characterized by pain and numbness in the buttocks and thighs after walking a short distance, then being able to walk again after taking a short break.
Treatment at our clinics
Our clinic offers the Cellgel method, a treatment that repairs the damaged disc.
Even if actual treatment is performed to relieve the symptoms, if the cracks in the disc are not successfully repaired, there is a definite possibility that the disc may herniate again or that the spinal canal narrows again.
Our Cellgel method injects a chemical compound that fills up the cracks in the disc, and then turns into a gel that repairs the cracks, thus providing a treatment at root level. It is characterized by the fact that the volume of the disc is not reduced, and the medication remains in the disc as a gel-like implant after treatment, thus preserving the disc.
If you are suffering from back pain or have been diagnosed with disc degeneration, please consider reserving a consultation at our clinic.