Column The Different Types of Disc Herniation Surgery and How to Choose the Right One For You
May 23, 2025
The most frequent back pain disorder in patients is lumbar disc herniation.
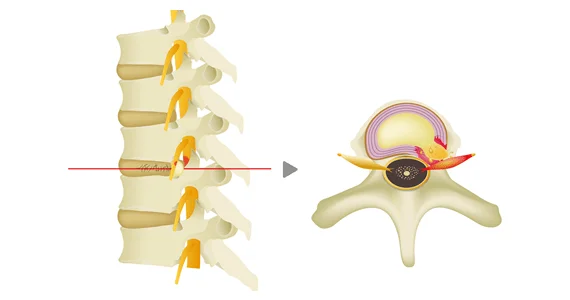
A disc herniation can cause a variety of symptoms, including pain and numbness in the buttocks and legs as well as back pain. When this happens, the spine bends sideways, making it difficult to move, and the pain can be more intense when lifting heavy objects, which can interfere with daily life.
In this article, we will discuss surgery for lumbar disc herniation.
Surgery for disc herniation
Surgical procedures
・The LOVE Method
This method has been commonly used in the past as a surgical procedure for disc herniation. An incision of 5 cm to 10 cm is made in the back under general anesthesia, and a portion of the ligament or vertebral arch is removed while carefully avoiding the nerves, and the herniated area is removed.
The surgery is performed under fluoroscopy, so lesions are easily visible, but the incisions tend to be quite extensive, resulting in a heavy strain on the body and requiring a lengthy hospital stay of two to three weeks.
・Microendoscopic Discectomy (MED)
An incision of about 16 mm is made in the back under general anesthesia, an endoscope is inserted through an external tube, and is used to monitor the location of the herniated area to remove the protruding herniated area.
In contrast to the LOVE method, less muscle is cut and postoperative pain is minimal. The postoperative scar is also smaller than that of the LOVE method, and the hospitalization period is about 1 to 2 weeks.
・Percutaneous Endoscopic Herniectomy (PELD)
PELD surgery may be considered when the area of the disc herniation is extensive and the symptoms are more severe. In this case, a tube called an operation tube is inserted through the back under local anesthesia, and the hernia is removed through the tube while monitoring the herniated area through an endoscope. The incision is small, the postoperative scar is hardly noticeable, and postoperative pain is minimal.
However, it is quite tricky to perform the PELD Method when the intervertebral space is narrow or when spinal canal stenosis or spondylolisthesis has occured in combination with the hernia.
・Spinal fusion surgery
Spinal fusion is performed when spondylolisthesis or spinal instability are involved. Under general anesthesia, an incision of about 2-3 cm is made in the back, the herniated disc itself is removed, and the upper and lower vertebrae are fused together with screws and rods by placing a titanium cage between them.
Currently, the surgery is performed using an endoscope, but once in place, movement of the lower back becomes limited. A period of hospitalization of one to two weeks is required.
Intervertebral disc treatment
In contrast to the standard surgical procedure that consists in removing the herniated area, disc therapy, which approaches the damaged disc, has been used in recent years.
Unlike surgery, hospitalization is not required, and in some cases, treatment can be performed as an ambulatory procedure.
・Intradiscal Enzyme Injection Therapy (Hernicore)
Intradiscal enzyme injection therapy involves injecting an enzyme-containing agent into the disc, which changes the composition of the disc and causes the herniation to disappear. It usually requires one to two days of hospitalization. Intradiscal enzyme injection therapy can only be performed once in a lifetime, and a second treatment on the same disc is not possible.
・Percutaneous Laser Disc Decompression (PLDD)
A needle is inserted into the affected disc herniation area from the back under local anesthesia, and a laser fiber is passed through the path of the needle. The laser burns the nucleus pulposus in the disc, creating a cavity in the nucleus pulposus and causing the disc to shrink. This treatment is effective not only for mild disc herniation but also for nonspecific low back pain.
・Percutaneous Ozone Disc Decompression (PODD)
This treatment is indicated for mild herniation that does not require surgery and does not respond to conventional conservative treatment.
Accessing from the back, a needle is inserted into the affected disc under local anesthesia, and a mixture of ozone gas and oxygen is injected through the tip of the needle. Ozone oxidation reduces the volume of the disc herniation and relieves pressure on the nerves. This also has an anti-inflammatory effect on the affected area.
・The Cellgel Method ( Gel Implant for Intervertebral Disc Repair)
This is one of the advanced treatment methods that have been researched and developed in recent years, and is one of the newest treatment methods backed with solid evidence.
It constitutes a fundamental treatment because it enables “disc repair,” which had not been achieved with other treatment methods to date. It is characterized by the fact that the volume of the disc is not reduced and the drug remains in the disc as a gel-like implant after treatment, thus preserving the disc.
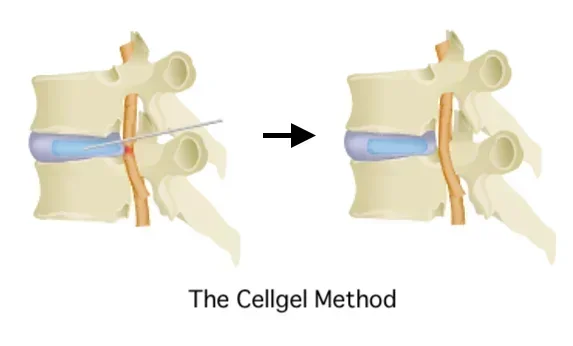
It can be applied not only to herniated discs but also to a wide range of other disorders, and even on patients who have had surgery before but are still in pain, or whose pain has recurred, or elderly patients over 80 years old can undergo the treatment.
How to choose surgery for disc herniation
Severity of the symptoms
The severity of pain and numbness, as well as the presence or absence of other symptoms, is one of the main criteria for choosing the appropriate type of treatment.
If the patient is experiencing only mild pain, conservative treatment is generally indicated instead of surgery. If imaging findings confirm a mild herniation, disc treatment such as laser or ozone therapy may be indicated.
Surgical treatment may be considered if there is severe numbness, gait disturbance, or interference with daily activities. Surgery is also suggested if no improvement is seen after 6 months of conservative treatment.
Existence of other medical conditions
If there are accompanying pathologies other than disc herniation (e.g., spondylolisthesis, lumbar instability, etc.), surgery involving more invasive procedures, such as spinal fusion, may be necessary.
If the patient has pre-existing medical conditions such as high blood pressure or diabetes, the type of surgery will be selected based on whether the patient can tolerate general anesthesia and whether it will interfere with postoperative rehabilitation.
Return to work after surgery
When choosing surgery for disc herniation, one of the factors to consider is the process of one’s postoperative return to work. Conventional surgery involves a period of hospitalization after surgery and may require bed rest for a certain period of time. If the patient cannot take time off work or has no one to help with housework or other tasks, the patient may choose to undergo a one-day procedure that does not require hospitalization.
Cost
Depending on the medical facility and the type of surgery, insurance may cover the procedure (conventional surgery) or it may not (disc treatment performed in recent years).
Conventional surgery requires a period of hospitalization, and the cost of hospitalization is separate from the cost of treatment. The longer the hospital stay, the higher the cost.
Fundamental treatment or otherwise
One of the factors to consider when choosing a surgery is whether or not the surgery is a fundamental treatment.
Disc herniation is a condition in which the nucleus pulposus protrudes outward due to a fissure in the annulus fibrosus. If only the herniated part is removed, the fissure in the annulus fibrosus will not heal and there is a high risk that the disc will herniate again.
If fundamental treatment is the desired outcome, it is a good idea to consider a treatment that replaces the cracks in the disc.
Postoperative care consecutive to disc herniation surgery
Once you have undergone surgery on a herniated lumbar disc, getting a good postoperative care is also essential.
Although it may vary depending on the type of surgery, it is best to avoid postures and movements that put strain on the lower back for a certain period of time after the surgery.
After a certain period of time has passed, it is important to conduct rehabilitation. This will help to reduce the strain on the lower back while strengthening the muscles around it, helping with the recovery process. The important thing is to continue rehabilitation in a consistent manner. If you interrupt your rehabilitation, your body may become easily strained, and your symptoms may recur.
If you have been diagnosed with disc herniation in the past, please consider visiting our clinic for a consultation.
Related articles
Understanding Disc Herniation and Receiving the Most Appropriate Treatment For It
What is Lumbar Disc Herniation? Causes of Pain and Symptoms
Is Disc Herniation for Teens and Young Adults on The Rise?
Symptoms and Treatments of Disc Herniation: When Early Detection is Key
How to Prevent Disc Herniation: Important Points to Keep in Mind in Your Daily Life
Professional Athletes Who Have Battled With Disc Herniation in the Past – vol.1 – Kensuke Kondo
Professional Athletes Who Have Battled With Disc Herniation in the Past – vol.2 – Sani Brown
Professional Athletes Who Have Battled With Disc Herniation in the Past – vol.3 – Yuto Nagatomo