Column Various Treatments for Lumbar Disc Herniation: Respective Differences and Results of Each Method
June 30, 2023
The most common back pain disorder is lumbar disc herniation.
A herniated disc can cause not only back pain, but also various symptoms such as pain and numbness in the buttocks and legs. The spine bends sideways, making it difficult to move, and the pain may intensify when lifting heavy objects, which interferes with daily life.
Treatment varies widely, including drug therapy, exercise therapy, nerve blocks, surgery, and intervertebral disc therapy.
Here we will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each treatment for lumbar disc herniation.
Treatments of Herniated Discs
Treatment of lumbar disc herniation can be broadly divided into conservative therapy and surgery.
Conservative therapy
Once a herniated disc has been diagnosed, conservative therapy is the first step in most cases.
Medication
Medications include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesics (such as Loxonin and Voltaren), muscle relaxants, opioid analgesics (such as morphine), and neuroleptics to reduce inflammation and pain.
These drugs may relieve pain and other symptoms.
However, because the drug therapy must be continued until the symptoms disappear, the patient is required to take the medications for a long period of time.
Patients with pre-existing medical conditions may not be able to receive drug therapy, so a consultation with their treating doctor is needed.
Nerve blocks
Nerve blocks are performed when drug therapy is ineffective or when the pain is severe.
Nerve blocks are effective in relieving pain in a specific area by neutralizing the nerves.
However, it is important to note that prolonged block injections may end up damaging the nerves.
Exercise therapy
Exercise therapy relieves pain and other symptoms by strengthening the muscles.
It is also beneficial to use exercise therapy to prevent recurrence after undergoing various treatments, such as surgery.
The important point is to continue to exercise in a consistent and moderate manner, as failing to do so may aggravate back pain instead.
Conservative therapy is basically effective for herniated discs in its early stage.
If symptoms do not disappear after several months of conservative treatment, surgical treatment may have to be considered.
Surgery
Surgery for lumbar disc herniation varies depending on the medical facilities.
The most commonly performed are the LOVE, MED, and PELD methods. The end result is basically the same: to relieve symptoms by removing the herniation itself, the only difference being in the chosen surgical method.
Hemi-semi-laminectomy (known as the L.O.V.E. procedure in Japan)
The LOVE method has been commonly used for herniated disc surgery in the past, and is a hernia removal procedure that is performed while the disc is in plain view at all times during the procedure. A 5 cm to 10 cm incision is made in the back under general anesthesia, and a portion of the ligament or vertebral arch is removed while avoiding the nerves, or the herniated area is excised. While the visual observation of the surgery minimizes the risk of missing a lesion, the wide incision causes a heavy strain on the body and prolongs the hospital stay to 2 to 3 weeks.
Micro Endoscopic Discectomy(MED)
Unlike the LOVE method, since the area of muscles to be cut is small, it results in minimal postoperative pain. The postoperative scar is smaller than that of the LOVE method, and the hospitalization period is about one to two weeks.
percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy(PELD)
PELD surgery may be performed when the size of the herniated disc is large and the patient is in a great deal of pain. Under local anesthesia, a tube called an operation tube is inserted through the back, and the herniated disc is removed through the tube while checking the herniated area through an endoscope. As the incision is small, the postoperative scar is hardly visible, and postoperative pain is minimal.
However, it is said that the PELD method is difficult to perform when the intervertebral space is narrow or in the presence of complications caused by spinal canal stenosis or spondylolisthesis.
Percutaneous Ozone Disc Decompression (PODD)
PODD is indicated for mild herniation that does not require surgery and does not respond to conventional conservative treatment.
A needle is inserted into the herniated disc from the back under local anesthesia, and a mixture of ozone and oxygen is injected through the tip of the needle. Ozone oxidation then reduces the volume of the herniated disc and relieves compression on the nerve. It also has an anti-inflammatory effect on the affected area, which reduces the risk of side effects and complications.
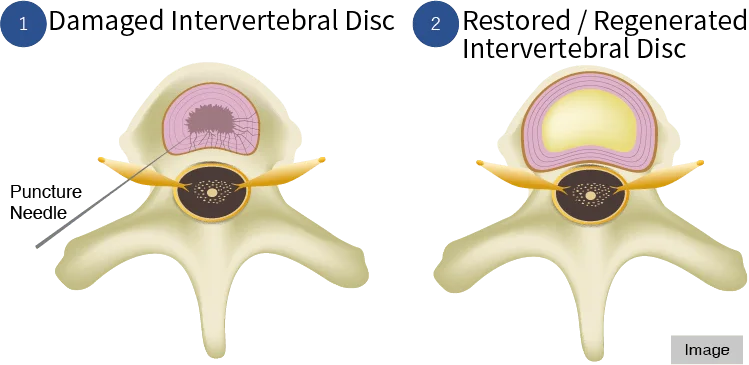
The Cellgel method (use of a gel-like implant to repair the disc)
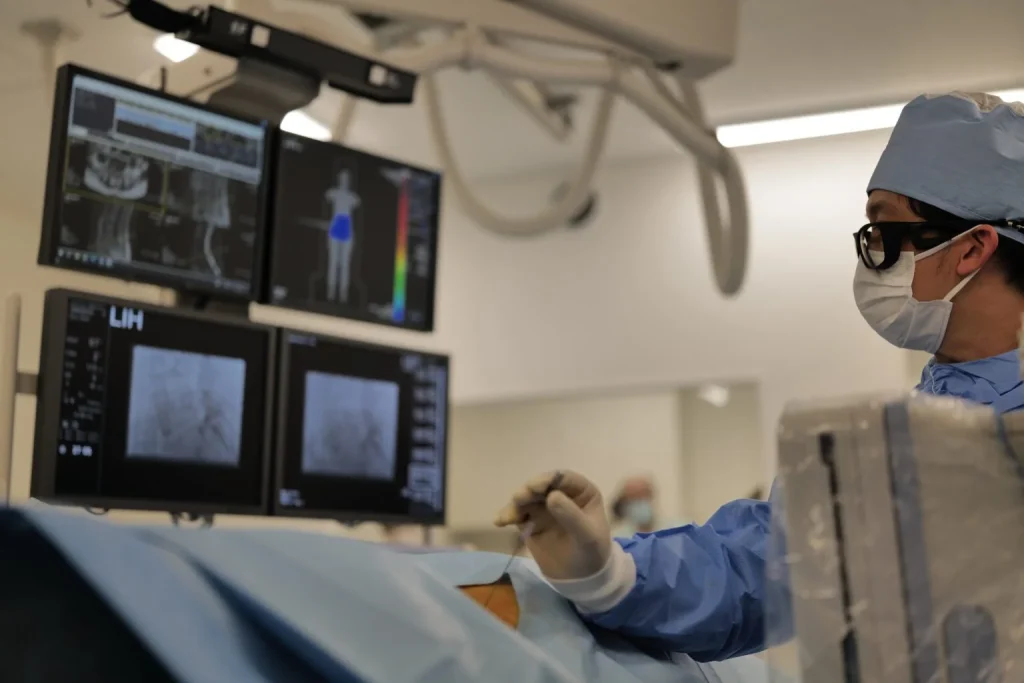
This is one of the advanced treatment methods that have been researched and developed in recent years, and is a newer treatment method that is backed by solid evidence.
It is a curative treatment because it has the ability to”repair the disc,” which is not possible with other treatment methods. It is characterized by the fact that the volume of the disc is not reduced by the procedure and the agent remains in the disc as a gel-like implant after treatment, thus preserving the disc.
It can be applied not only to herniated discs but also to a wide range of other conditions. In addition, it can be used for patients who have felt any pain relief consecutive to surgery, or who have experienced a recurrence of pain, as well as for elderly patients over 80 years of age.
If you have been diagnosed with disc herniation and are in pain, if you want to avoid spinal surgery, or if your herniation has recurred, please visit our clinic for a consultation.
Related Articles
Disc herniation
Understanding Disc Herniation and Receiving the Most Appropriate Treatment For It