November 7, 2025
Lumbar disc herniation (LDH) can occur regardless of age. While the typical age of onset is 20 to 40 years old, it can affect young people as early as their teens.
In this article, we explain five common traits and lifestyle factors that increase the risk of developing a lumbar disc herniation.
What Is Lumbar Disc Herniation?
Between each pair of vertebrae lies an intervertebral disc, composed of a gelatinous center called the nucleus pulposus surrounded by a tough outer ring known as the annulus fibrosus, which is rich in collagen.
When the annulus fibrosus tears and part of the nucleus pulposus protrudes outward, this condition is known as a herniated disc.
The main symptoms of lumbar disc herniation include low back pain, as well as pain or numbness in the buttocks or legs.
While the symptoms can appear anywhere in the lower body, pain radiating from the buttocks down the back of the thigh (sciatica) is especially common.
The intervertebral disc lies between the vertebrae. It consists of a gelatinous center called the nucleus pulposus, surrounded by a collagen-rich outer ring called the annulus fibrosus.
Disc herniation occurs when the nucleus pulposus protrudes or ruptures out through a tear in the annulus fibrosus.
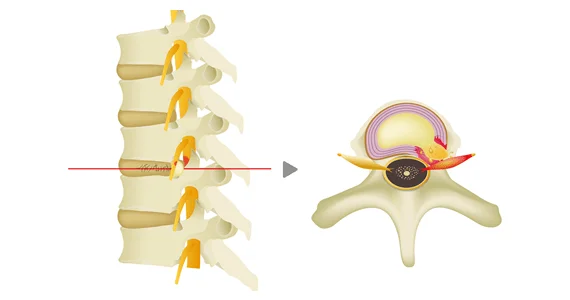
The main symptoms of a lumbar disc herniation are low back pain accompanied by pain or numbness in the buttocks and legs. Pain and numbness can occur anywhere in the lower body, but pain radiating from the buttocks to the back of the thigh—known as sciatica—is a classic symptom of a lumbar herniation.
Predisposing Factors for Disc Herniation
Body Type
Obesity is a recognized factor that can lead to disc degeneration, thickening of spinal ligaments, disc herniation, and spinal stenosis (*1).
The higher the BMI, the more susceptible a person is to disc herniation, as increased body weight places constant, excessive strain on the discs.
(*1): Schumann B., et al. Lifestyle factors and lumbar disc disease: Results of a German multi-center case-control study (EPILIFT). Arthritis Research & Therapy. 2010, 12(5).
Posture
Daily posture significantly impacts how pressure is distributed across the discs, raising the risk of herniation.
Rounded back and forward head posture (kyphosis): places pressure on the front of the disc, causing the nucleus to protrude backward.
Excessive arch in the lower back (hyperlordosis): increases stress on the back of the disc and facet joints.
Asymmetric posture (leaning or carrying weight on one side): creates uneven pressure, overloading one side of the spine.
Additionally, maintaining the same position for prolonged periods—for example, during desk work or prolonged driving—can also increase risk.
Lack of Exercise
Insufficient physical activity leads to weakened core muscles, reducing spinal support.
As muscle strength declines, nutrient delivery to the discs decreases, accelerating degeneration and increasing the risk of herniation.
Smoking
Smoking is a major contributing factor to disc herniation, confirmed by numerous studies (*2).
Nicotine inhibits collagen production in the annulus fibrosus. The reduction in collagen makes the disc more prone to degeneration and herniation.
Smoking is also reported to increase the risk of disc herniation recurrence and the need for reoperation.
(*2): Akmal, M., Kesani, A., Anand, B., Singh, A., Wiseman, M., & Goodship, A. Effect of Nicotine on Spinal Disc Cells: A Cellular Mechanism for Disc Degeneration. Spine. 2004, 29(5). Andersen, S. B., Smith, E. C., Støttrup, C., Carreon, L. Y., & Andersen, M. O. Smoking Is an Independent Risk Factor of Reoperation Due to Recurrent Lumbar Disc Herniation. Global Spine Journal. 2017, 8(4).
High-Impact Sports and Physical Activities
Sports that involve frequent twisting, bending, or hyperextension of the lower back (such as baseball, soccer, and gymnastics) increase the risk of disc herniation.
These repetitive movements put significant stress on the lumbar joints and muscles, making the discs more susceptible to injury.
Our Clinic’s Treatment: The Cellgel Method
At ILC International Low Back Pain Clinic, we treat lumbar disc herniation using the Cellgel Method, a minimally invasive procedure that repairs damaged intervertebral discs.
This treatment involves injecting a liquid agent into the cracked portion of the disc.
The agent then solidifies into a gel-like implant, sealing the fissure and restoring disc integrity, effectively providing a fundamental treatment..
Unlike conventional procedures that may reduce disc volume, the Cellgel Method preserves disc structure while alleviating pain.
👉 Click Here to Learn More About the Cellgel Method
We offer free MRI image consultations.
If you already have lumbar MRI images taken at another hospital, please feel free to contact us for evaluation and advice.
👉 Clich Here For a Free MRI Imaging Consultation
If you have been diagnosed with a disc herniation or suffer from chronic back pain, please consider a consultation with us.
Related Articles
Understanding Herniated Discs and Receiving the Most Appropriate Treatment For It
5 Medical Conditions That Can Be Easily Confused with Disc Herniation
Can Disc Herniation Heal Naturally?
Symptoms and Treatments of Disc Herniation: When Early Detection is Key
Various Treatments for Lumbar Disc Herniation: Respective Differences and Results of Each Method
Is Disc Herniation for Teens and Young Adults on The Rise?
What Is a Lumbar Disc Herniation and Why Is an MRI Necessary? Understanding How Diagnosis Is Made
Prevention Rather Than Intervention: Precautions to Take to Prevent Disc Herniation