Column Disc Herniation: How Often Do You Need to Visit A Clinic Depending on The Treatment?
January 16, 2026
Lumbar disc herniation is a condition that can occur at any age.
As the condition progresses, pain and numbness can significantly interfere with your daily life.
In this article, we explain lumbar disc herniation and the recommended frequency of clinic visits.
What Is Lumbar Disc Herniation?
The intervertebral disc acts as a cushion between the vertebrae. It consists of a jelly-like center called the nucleus pulposus, surrounded by a tough outer layer rich in collagen called the annulus fibrosus.
When a tear develops in the annulus fibrosus and the nucleus pulposus protrudes outward, this condition is referred to as disc herniation.
The main symptoms of lumbar disc herniation include low back pain, as well as pain and numbness in the buttocks and legs.
Pain and numbness may appear anywhere in the lower extremities, but sciatica — pain radiating from the buttocks down the back of the thigh — is a characteristic symptom of lumbar disc herniation.
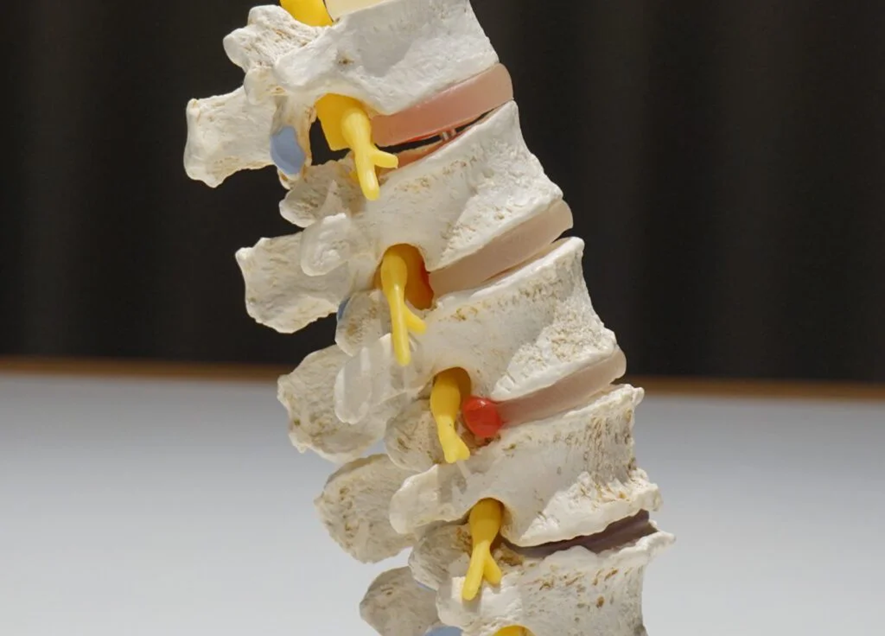
Frequency of Clinic Visits for Lumbar Disc Herniation by Treatment Type
Once diagnosed with lumbar disc herniation, the frequency of clinic visits will vary depending on symptom severity and treatment method.
Conservative Therapy
During the acute phase when pain is most intense, frequent visits (2–4 times a week) are recommended to manage inflammation and relieve nerve pressure through medication or physical therapy.
As symptoms improve, visit frequency may be gradually reduced to once per week or once every two weeks, depending on the patient’s condition.
Surgical Procedures
When surgical treatment for lumbar disc herniation is indicated, one to several outpatient visits are required prior to surgery.
Once surgery is scheduled, hospitalization typically begins the day before surgery.
The length of hospitalization varies depending on the surgical technique and medical facility:
- Several days for PED (Percutaneous Endoscopic Discectomy)
- Approximately one week for MED (Microendoscopic Discectomy)
- Approximately two weeks for spinal fusion surgery
After surgery and discharge, patients usually require weekly rehabilitation sessions, as well as follow-up visits once a month or once every few months.
Minimally Invasive One-day Treatment
In recent years, same-day minimally invasive treatments for lumbar disc herniation, such as the Cellgel Method, designed for busy individuals, have become available.
Both consultation and treatment can be completed in a single day, and routine post-treatment clinic visits are generally not required.
However, even after treatment, regular rehabilitation is recommended to address muscle-related pain and to support functional recovery.
Our Clinic’s Treatment
Our clinic specializes in the Cellgel Method, a fundamental treatment designed to repair damaged intervertebral discs in patients with lumbar disc herniation.
With the Cellgel Method, a therapeutic agent is injected into the cracked portion of the disc, where it turns into a gel and reinforces the damaged area. This allows for causal (fundamental) treatment of the condition.
Because disc volume is preserved and the gel remains within the disc as an implant after treatment, the intervertebral disc itself is conserved, which is a key feature of this therapy.
Learn more about the Cellgel Method
If you are worried about the time commitment of traditional surgery or the endless cycle of conservative therapy visits, minimally invasive day treatments may be the right solution for you.
Related Articles
Understanding Herniated Discs and Receiving the Most Appropriate Treatment For It
What is Lumbar Disc Herniation? Causes of Pain and Symptoms
Various Treatments for Lumbar Disc Herniation: Respective Differences and Results of Each Method
Is Disc Herniation for Teens and Young Adults on The Rise?
Symptoms and Treatments of Disc Herniation: When Early Detection is Key
Can Disc Herniation Heal Naturally?
How to Prevent Recurrence After Disc Herniation Surgery? Lifestyle Habits and Posture Are Key
Balancing Work and Disc Herniation: Key Points for Adjusting Your Work Style