April 04, 2025
Lumbar disc herniation is the most prevalent spine disorder.
In this article, we will discuss how to diagnose disc herniation and where to go from there.
What is disc herniation?
Intervertebral discs are located between each vertebra. These discs have a gelatinous nucleus pulposus in the center and a collagen-rich annulus fibrosus that encapsulates the nucleus pulposus.
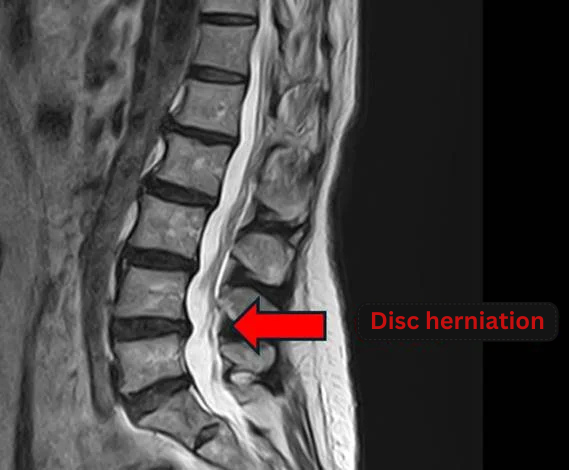
A crack in the annulus fibrosus will cause the nucleus pulposus to protrude outward, resulting in disc herniation.
When the nucleus pulposus protrudes, it induces a loss in the disc function. This increases the strain on the spine and begins to deform the spine and ligaments, causing intervertebral arthritis and ligament ossification, which can lead to spinal canal stenosis and intervertebral foramen stenosis.
Diagnosis of disc herniation
Diagnosis of disc herniation involves physical examination and an assessment of the symptoms, as well as looking at imaging tests such as X-rays and MRIs. Among these, medical examination and MRI are considered essential for the diagnosis of disc herniation.
Diagnostic Imaging – X-rays and MRI
X-ray images serve primarily to show the condition of the bones. Since the intervertebral discs, which are cartilage, do not show up on X-rays, it is impossible to diagnose a herniated disc based on that alone. However, X-rays are essential to confirm that there is no other condition besides disc herniation that could be the cause of the back pain.
MRI scans are the most widely used procedure to diagnose disc herniation; MRI images are used to check for deformity in the disc, nerve, ligaments, and the joint areas associated with back pain factors, pressure on the nerves, the presence or absence of damage, and inflammation.
Examination during the consultation
In addition to the imaging examination, a physical examination is performed during the consultation. The presence of disc herniation or spinal canal stenosis are assessed by having the patient bend forward and backward in succession and checking the resulting symptoms.
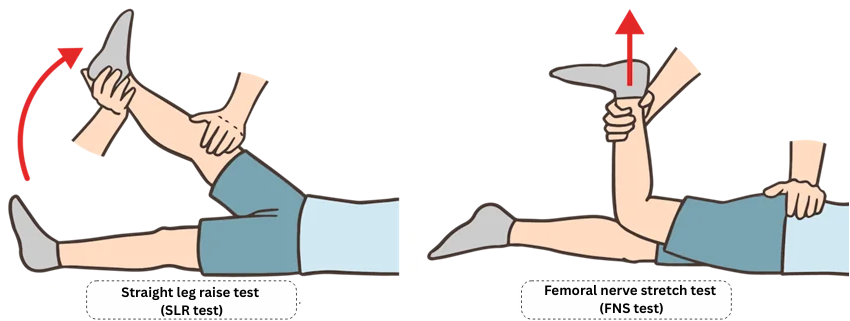
We also check for leg pain by lifting the patient’s leg with the straight leg raise test (SLR test) and the femoral nerve stretch test (FNS test). If pain is observed when performing these tests, then there is lumbar disc herniation.
Early diagnosis of disc herniation is critical
In the case of mild disc herniation, symptoms may not be perceptible or strong. If the herniated disc is left untreated, the herniation will progress and symptoms will become more severe, eventually leading to severe symptoms (e.g., difficulty walking).
Once this happens, treatment options become limited, and recovery may be slow or insufficient even following treatment.
It is very important to receive an appropriate diagnosis before the symptoms become severe, since an early diagnosis will ensure an appropriate treatment and an earlier reintegration into society.
Measures to implement following diagnosis
Once disc herniation has been diagnosed, the first step in most cases is conservative treatment. Medications include neuroleptics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesics, muscle relaxants, and opioid analgesics to improve pain and inflammation. Physical therapy may also be used to improve back pain. Nerve blocks may be used if the pain is severe.
If conservative treatment fails to improve the pain, laser treatment or discectomy may be considered. If the herniation is advanced and the presence of spinal canal stenosis or spondylolisthesis is also confirmed, spinal fusion surgery may be performed to remove the herniated disc itself and replace it with an artificial one that will be affixed to the upper and lower vertebrae.
Treatment at our clinic
Once a herniated disc is diagnosed, it is important not to leave it untreated but to have it diagnosed by a specialist. Early detection and appropriate treatment can prevent the condition from worsening and even cure it completely.
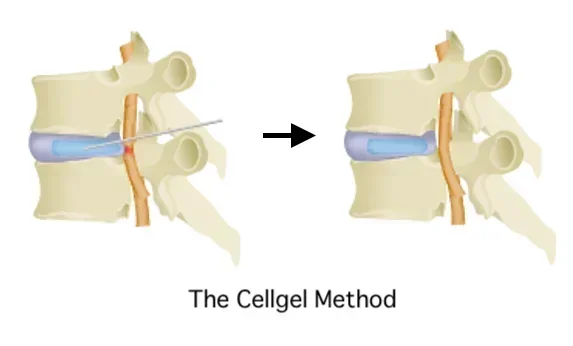
Our clinic offers the Cdellgel Method, a treatment that repairs damaged discs.
With our Cellgel Method, a drug is injected and fills the cracks in the disc, and then turns into a gel that mends the cracks, thus providing a fundamental cure. It is characterized by the fact that the volume of the disc is not reduced and the drug remains in the disc as a gel-like implant after treatment, thus preserving the disc.
If you have been diagnosed with a herniated disc, please consider a consultation with us.
Related Articles
Understanding Disc Herniation and Receiving the Most Appropriate Treatment For It
What is Lumbar Disc Herniation? Causes of Pain and Symptoms
Various Treatments for Lumbar Disc Herniation: Respective Differences and Results of Each Method
Is Disc Herniation for Teens and Young Adults on The Rise?
Symptoms and Treatments of Disc Herniation: When Early Detection is Key
How to Prevent Disc Herniation: Important Points to Keep in Mind in Your Daily Life
Postoperative Rehabilitation for Disc Herniation: The Road to Success